Working with multiple endpoints
2019-10-17
Source:vignettes/multiple-endpoints.Rmd
multiple-endpoints.Rmd
nlmixr
Multiple endpoints
Joint PK/PD models, or PK/PD models where you fix certain components are common in pharmacometrics. A classic example, (provided by Tomoo Funaki and Nick Holford) is Warfarin.
In this example, we have a transit-compartment (from depot to gut to central volume) PK model and an effect compartment for the PCA measurement.
Below is an illustrated example of a model that can be applied to the data:
pk.turnover.emax <- function() {
ini({
tktr <- log(1)
tka <- log(1)
tcl <- log(0.1)
tv <- log(10)
##
eta.ktr ~ 1
eta.ka ~ 1
eta.cl ~ 2
eta.v ~ 1
prop.err <- 0.1
pkadd.err <- 0.1
##
poplogit <- 2
#temax <- 7.5
tec50 <- log(0.5)
tkout <- log(0.05)
te0 <- log(100)
##
eta.emax ~ .5
eta.ec50 ~ .5
eta.kout ~ .5
eta.e0 ~ .5
##
pdadd.err <- 10
})
model({
ktr <- exp(tktr + eta.ktr)
ka <- exp(tka + eta.ka)
cl <- exp(tcl + eta.cl)
v <- exp(tv + eta.v)
##
#poplogit = log(temax/(1-temax))
logit=exp(poplogit+eta.emax)
#logit=temax+eta.emax
emax = logit/(1+logit)
ec50 = exp(tec50 + eta.ec50)
kout = exp(tkout + eta.kout)
e0 = exp(te0 + eta.e0)
##
DCP = center/v
PD=1-emax*DCP/(ec50+DCP)
##
effect(0) = e0
kin = e0*kout
##
d/dt(depot) = -ktr * depot
d/dt(gut) = ktr * depot -ka * gut
d/dt(center) = ka * gut - cl / v * center
d/dt(effect) = kin*PD -kout*effect
##
cp = center / v
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)
effect ~ add(pdadd.err)
})
}Notice there are two endpoints in the model cp and effect. Both are modeled in nlmixr using the ~ “modeled by” specification.
To see more about how nlmixr will handle the multiple compartment model, it is quite informative to parse the model and print the information about that model. In this case an initial parsing would give:
ui <- nlmixr(pk.turnover.emax)
ui
#> ▂▂ RxODE-based ODE model ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
#> ── Initialization: ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> Fixed Effects ($theta):
#> tktr tka tcl tv poplogit tec50
#> 0.0000000 0.0000000 -2.3025851 2.3025851 2.0000000 -0.6931472
#> tkout te0
#> -2.9957323 4.6051702
#>
#> Omega ($omega):
#> eta.ktr eta.ka eta.cl eta.v eta.emax eta.ec50 eta.kout eta.e0
#> eta.ktr 1 0 0 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
#> eta.ka 0 1 0 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
#> eta.cl 0 0 2 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
#> eta.v 0 0 0 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
#> eta.emax 0 0 0 0 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0
#> eta.ec50 0 0 0 0 0.0 0.5 0.0 0.0
#> eta.kout 0 0 0 0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0
#> eta.e0 0 0 0 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5
#> ── Multiple Endpoint Model ($multipleEndpoint): ───────────────────────────
#> ┌───────────────────────┬───────────────────────┬───────────────────────┐
#> │ variable │ cmt │ dvid* │
#> ├───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
#> │ cp ~ … │ cmt='cp' or cmt=5 │ dvid='cp' or dvid=1 │
#> ├───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
#> │ effect ~ … │ cmt='effect' or cmt=4 │ dvid='effect' or │
#> │ │ │ dvid=2 │
#> └───────────────────────┴───────────────────────┴───────────────────────┘
#> * If dvids are outside this range, all dvids are re-numered
#> sequentially, ie 1,7, 10 becomes 1,2,3 etc
#> ── μ-referencing ($muRefTable): ───────────────────────────────────────────
#> ┌──────────┬──────────┐
#> │ theta │ eta │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tktr │ eta.ktr │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tka │ eta.ka │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tcl │ eta.cl │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tv │ eta.v │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ poplogit │ eta.emax │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tec50 │ eta.ec50 │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ tkout │ eta.kout │
#> ├──────────┼──────────┤
#> │ te0 │ eta.e0 │
#> └──────────┴──────────┘
#> ── Model: ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> ktr <- exp(tktr + eta.ktr)
#> ka <- exp(tka + eta.ka)
#> cl <- exp(tcl + eta.cl)
#> v <- exp(tv + eta.v)
#> ##
#> #poplogit = log(temax/(1-temax))
#> logit=exp(poplogit+eta.emax)
#> #logit=temax+eta.emax
#> emax = logit/(1+logit)
#> ec50 = exp(tec50 + eta.ec50)
#> kout = exp(tkout + eta.kout)
#> e0 = exp(te0 + eta.e0)
#> ##
#> DCP = center/v
#> PD=1-emax*DCP/(ec50+DCP)
#> ##
#> effect(0) = e0
#> kin = e0*kout
#> ##
#> d/dt(depot) = -ktr * depot
#> d/dt(gut) = ktr * depot -ka * gut
#> d/dt(center) = ka * gut - cl / v * center
#> d/dt(effect) = kin*PD -kout*effect
#> ##
#> cp = center / v
#> cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)
#> effect ~ add(pdadd.err)
#> ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂In the middle of the printout, it shows how the data must be formatted (using the cmt and dvid data items) to allow nlmixr to model the multiple endpoint appropriately.
Of course if you are interested you can directly access the information in ui$multipleEndpoint.
ui$multipleEndpoint| variable | cmt | dvid* |
| cp ~ … | cmt='cp' or cmt=5 | dvid='cp' or dvid=1 |
| effect ~ … | cmt='effect' or cmt=4 | dvid='effect' or dvid=2 |
| * If dvids are outside this range, all dvids are re-numered sequentially, ie 1,7, 10 becomes 1,2,3 etc | ||
Notice that the cmt and dvid items can use the named variables directly as either the cmt or dvid specification. This flexible notation makes it so you do not have to rename your compartments to run nlmixr model functions.
The other thing to note is that the cp is specified by an ODE compartment above the number of compartments defined in the RxODE part of the nlmixr model. This is because cp is not a defined compartment, but a related variable cp.
The last thing to notice that the cmt items are numbered cmt=5 for cp or cmt=4 for effect even though they were specified in the model first by cp and cmt. This ordering is because effect is a compartment in the RxODE system. Of course cp is related to the compartment central, and it may make more sense to pair cp with the central compartment.
If this is something you want to have you can specify the compartment to relate the effect to by the | operator. In this case you would change
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)to
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err) | centralWith this change, the model could be updated to:
pk.turnover.emax2 <- function() {
ini({
tktr <- log(1)
tka <- log(1)
tcl <- log(0.1)
tv <- log(10)
##
eta.ktr ~ 1
eta.ka ~ 1
eta.cl ~ 2
eta.v ~ 1
prop.err <- 0.1
pkadd.err <- 0.1
##
poplogit <- 2
#temax <- 7.5
tec50 <- log(0.5)
tkout <- log(0.05)
te0 <- log(100)
##
eta.emax ~ .5
eta.ec50 ~ .5
eta.kout ~ .5
eta.e0 ~ .5
##
pdadd.err <- 10
})
model({
ktr <- exp(tktr + eta.ktr)
ka <- exp(tka + eta.ka)
cl <- exp(tcl + eta.cl)
v <- exp(tv + eta.v)
##
#poplogit = log(temax/(1-temax))
logit=exp(poplogit+eta.emax)
#logit=temax+eta.emax
emax = logit/(1+logit)
ec50 = exp(tec50 + eta.ec50)
kout = exp(tkout + eta.kout)
e0 = exp(te0 + eta.e0)
##
DCP = center/v
PD=1-emax*DCP/(ec50+DCP)
##
effect(0) = e0
kin = e0*kout
##
d/dt(depot) = -ktr * depot
d/dt(gut) = ktr * depot -ka * gut
d/dt(center) = ka * gut - cl / v * center
d/dt(effect) = kin*PD -kout*effect
##
cp = center / v
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err) | center
effect ~ add(pdadd.err)
})
}
ui2 <- nlmixr(pk.turnover.emax2)
ui2$multipleEndpoint| variable | cmt | dvid* |
| cp ~ … | cmt='center' or cmt=3 | dvid='center' or dvid=1 |
| effect ~ … | cmt='effect' or cmt=4 | dvid='effect' or dvid=2 |
| * If dvids are outside this range, all dvids are re-numered sequentially, ie 1,7, 10 becomes 1,2,3 etc | ||
Notice in this case the cmt variables are numbered sequentially and the cp variable matches the center compartment.
DVID vs CMT, which one is used
When dvid and cmt are combined in the same dataset, the cmt data item is always used on the event information and the dvid is used on the observations. nlmixr expects the cmt data item to match the dvid item for observations OR to be either zero or one for the dvid to replace the cmt information.
If you do not wish to use dvid items to define multiple endpoints in nlmixr, you can set the following option:
options(RxODE.combine.dvid=FALSE)
ui2$multipleEndpoint| variable | cmt |
| cp ~ … | cmt='center' or cmt=3 |
| effect ~ … | cmt='effect' or cmt=4 |
Then only cmt items are used for the multiple endpoint models. Of course you can turn it on or off for different models if you wish:
options(RxODE.combine.dvid=TRUE)
ui2$multipleEndpoint| variable | cmt | dvid* |
| cp ~ … | cmt='center' or cmt=3 | dvid='center' or dvid=1 |
| effect ~ … | cmt='effect' or cmt=4 | dvid='effect' or dvid=2 |
| * If dvids are outside this range, all dvids are re-numered sequentially, ie 1,7, 10 becomes 1,2,3 etc | ||
Running a multiple endpoint model
With this information, we can use the built-in warfarin dataset in nlmixr:
summary(warfarin)
#> id time amt dv
#> Min. : 1.00 Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0.000 Min. : 0.00
#> 1st Qu.: 8.00 1st Qu.: 24.00 1st Qu.: 0.000 1st Qu.: 4.50
#> Median :15.00 Median : 48.00 Median : 0.000 Median : 11.40
#> Mean :16.08 Mean : 52.08 Mean : 6.524 Mean : 20.02
#> 3rd Qu.:24.00 3rd Qu.: 96.00 3rd Qu.: 0.000 3rd Qu.: 26.00
#> Max. :33.00 Max. :144.00 Max. :153.000 Max. :100.00
#> dvid evid wt age sex
#> cp :283 Min. :0.00000 Min. : 40.00 Min. :21.00 female:101
#> pca:232 1st Qu.:0.00000 1st Qu.: 60.00 1st Qu.:23.00 male :414
#> Median :0.00000 Median : 70.00 Median :28.00
#> Mean :0.06214 Mean : 69.27 Mean :31.85
#> 3rd Qu.:0.00000 3rd Qu.: 78.00 3rd Qu.:36.00
#> Max. :1.00000 Max. :102.00 Max. :63.00Since dvid specifies pca as the effect endpoint, you can update the model to be more explicit making one last change:
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)
effect ~ add(pdadd.err) to
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)
effect ~ add(pdadd.err) | pcapk.turnover.emax3 <- function() {
ini({
tktr <- log(1)
tka <- log(1)
tcl <- log(0.1)
tv <- log(10)
##
eta.ktr ~ 1
eta.ka ~ 1
eta.cl ~ 2
eta.v ~ 1
prop.err <- 0.1
pkadd.err <- 0.1
##
poplogit <- 2
#temax <- 7.5
tec50 <- log(0.5)
tkout <- log(0.05)
te0 <- log(100)
##
eta.emax ~ .5
eta.ec50 ~ .5
eta.kout ~ .5
eta.e0 ~ .5
##
pdadd.err <- 10
})
model({
ktr <- exp(tktr + eta.ktr)
ka <- exp(tka + eta.ka)
cl <- exp(tcl + eta.cl)
v <- exp(tv + eta.v)
##
#poplogit = log(temax/(1-temax))
logit=exp(poplogit+eta.emax)
#logit=temax+eta.emax
emax = logit/(1+logit)
ec50 = exp(tec50 + eta.ec50)
kout = exp(tkout + eta.kout)
e0 = exp(te0 + eta.e0)
##
DCP = center/v
PD=1-emax*DCP/(ec50+DCP)
##
effect(0) = e0
kin = e0*kout
##
d/dt(depot) = -ktr * depot
d/dt(gut) = ktr * depot -ka * gut
d/dt(center) = ka * gut - cl / v * center
d/dt(effect) = kin*PD -kout*effect
##
cp = center / v
cp ~ prop(prop.err) + add(pkadd.err)
effect ~ add(pdadd.err) | pca
})
}Run the models with SAEM
fit.TOS <- nlmixr(pk.turnover.emax3, warfarin, "saem", control=list(print=0),
table=list(cwres=TRUE, npde=TRUE));
print(fit.TOS);
#> ── nlmixr SAEM([3mODE[23m); [2m[3mOBJF by FOCEi approximation[23m[22m fit ──────────────────────
#> OBJF AIC BIC Log-likelihood Condition Number
#> FOCEi 1397.183 2322.878 2402.298 -1142.439 1550.039
#>
#> ── Time (sec; $time): ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> saem setup table cwres covariance npde other
#> elapsed -342.842 401.1549 0.031 401.202 0.029 0.855 0.702141
#>
#> ── Population Parameters ($parFixed or $parFixedDf): ──────────────────────
#> Est. SE %RSE Back-transformed(95%CI) BSV(CV%)
#> tktr 0.265 0.285 107 1.3 (0.746, 2.28) 88.2
#> tka 0.0407 0.245 603 1.04 (0.644, 1.68) 58.4
#> tcl -2.01 0.0502 2.49 0.133 (0.121, 0.147) 27.9
#> tv 2.05 0.0442 2.16 7.73 (7.09, 8.43) 22.5
#> prop.err 0.116 0.116
#> pkadd.err 0.239 0.239
#> poplogit 2.95 0.445 15.1 19.2 (8.02, 45.9) 10.2
#> tec50 -0.0756 0.148 196 0.927 (0.693, 1.24) 53.0
#> tkout -2.87 0.0429 1.49 0.0565 (0.0519, 0.0614) 6.62
#> te0 4.57 0.012 0.262 96.6 (94.3, 98.9) 5.23
#> pdadd.err 4.08 4.08
#> Shrink(SD)%
#> tktr 48.4%
#> tka 52.1%
#> tcl 1.48%
#> tv 9.14%
#> prop.err
#> pkadd.err
#> poplogit 84.2%
#> tec50 6.17%
#> tkout 43.8%
#> te0 19.9%
#> pdadd.err
#>
#> Covariance Type ($covMethod): linFim
#> No correlations in between subject variability (BSV) matrix
#> Full BSV covariance ($omega) or correlation ($omegaR; diagonals=SDs)
#> Distribution stats (mean/skewness/kurtosis/p-value) available in $shrink
#>
#> ── Fit Data (object is a modified tibble): ────────────────────────────────
#> # A tibble: 483 x 42
#> ID TIME DV EVID CMT PRED RES WRES IPRED IRES IWRES CPRED
#> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 0.5 0 0 cp 1.50 -1.50 -0.564 0.484 -0.484 -1.97 1.05
#> 2 1 1 1.9 0 cp 4.16 -2.26 -0.849 1.57 0.329 1.09 3.24
#> 3 1 2 3.3 0 cp 8.57 -5.27 -1.91 4.21 -0.906 -1.67 7.80
#> # … with 480 more rows, and 30 more variables: CRES <dbl>, CWRES <dbl>,
#> # eta.ktr <dbl>, eta.ka <dbl>, eta.cl <dbl>, eta.v <dbl>,
#> # eta.emax <dbl>, eta.ec50 <dbl>, eta.kout <dbl>, eta.e0 <dbl>,
#> # ktr <dbl>, ka <dbl>, cl <dbl>, v <dbl>, logit <dbl>, emax <dbl>,
#> # ec50 <dbl>, kout <dbl>, e0 <dbl>, DCP <dbl>, PD <dbl>, kin <dbl>,
#> # cp <dbl>, depot <dbl>, gut <dbl>, center <dbl>, effect <dbl>,
#> # EPRED <dbl>, ERES <dbl>, NPDE <dbl>SAEM Diagnostic plots
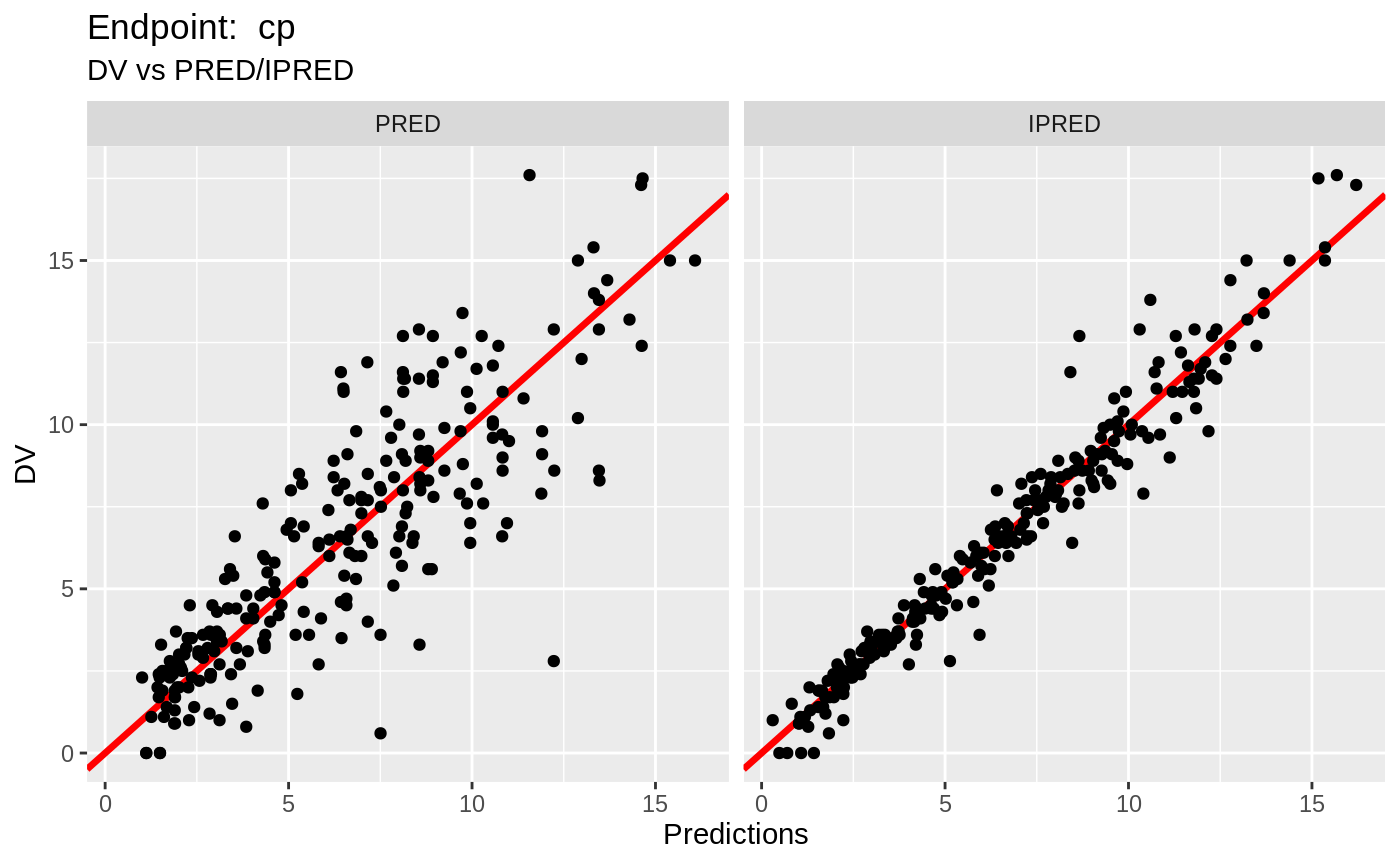
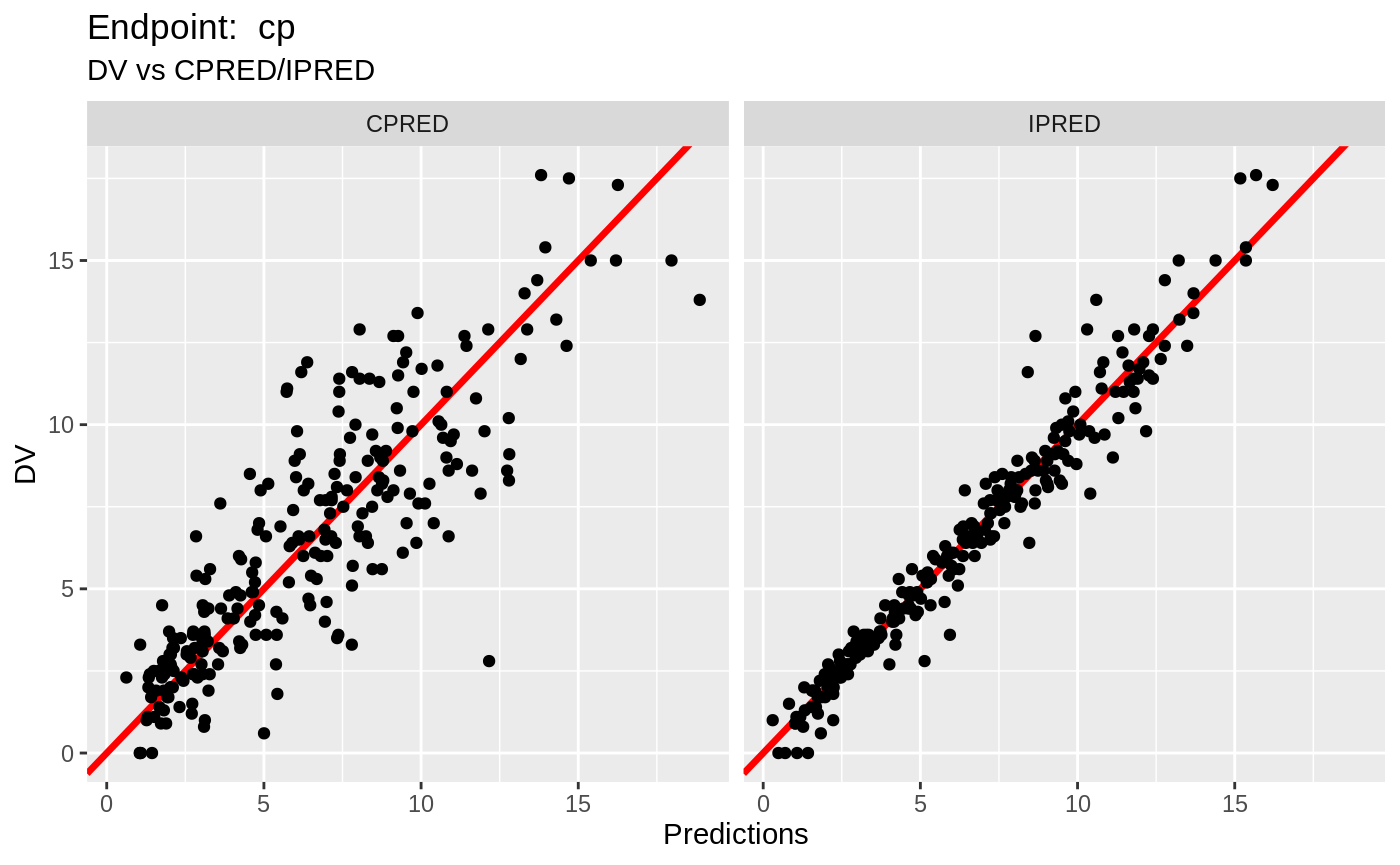
plot(fit.TOS);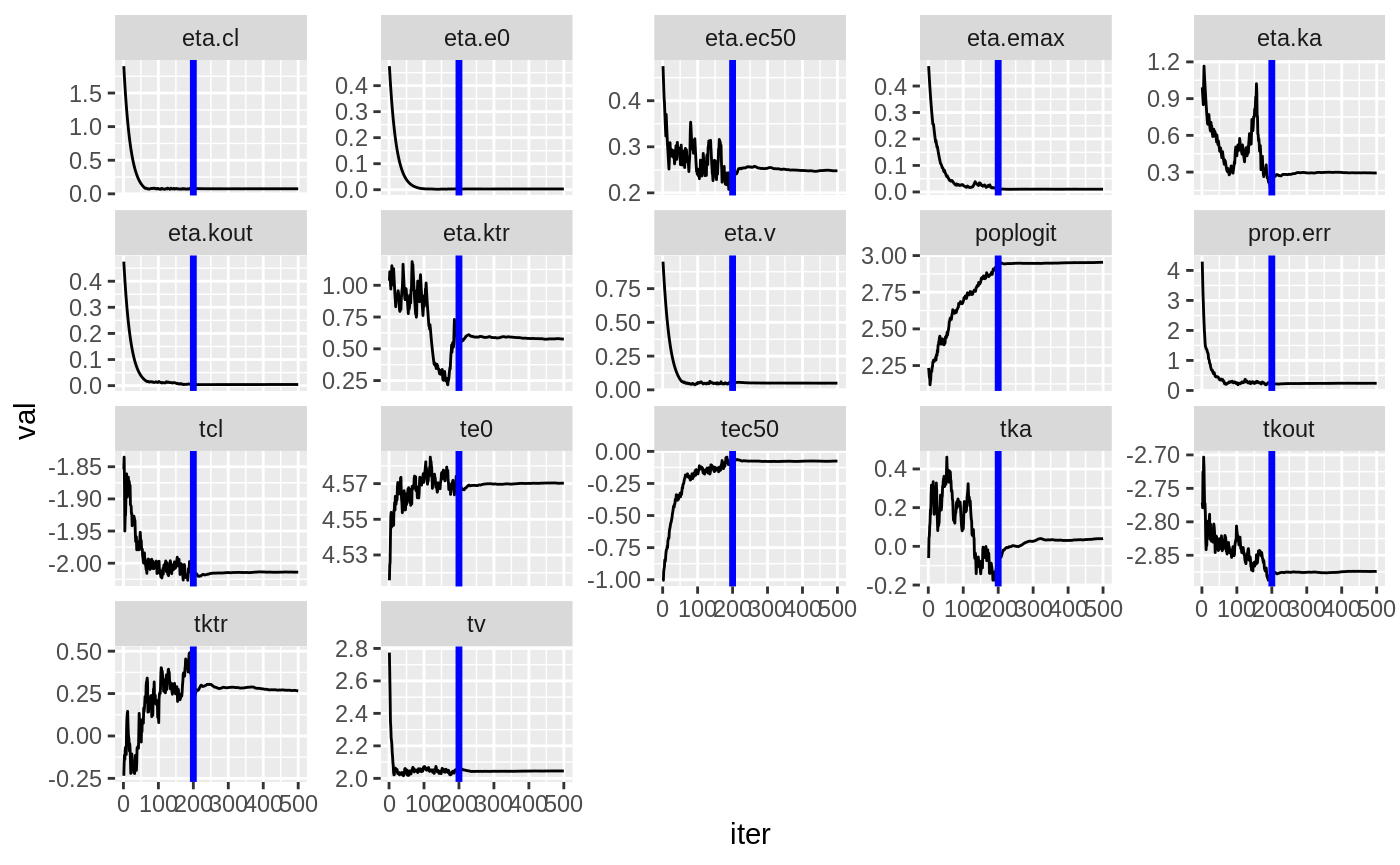
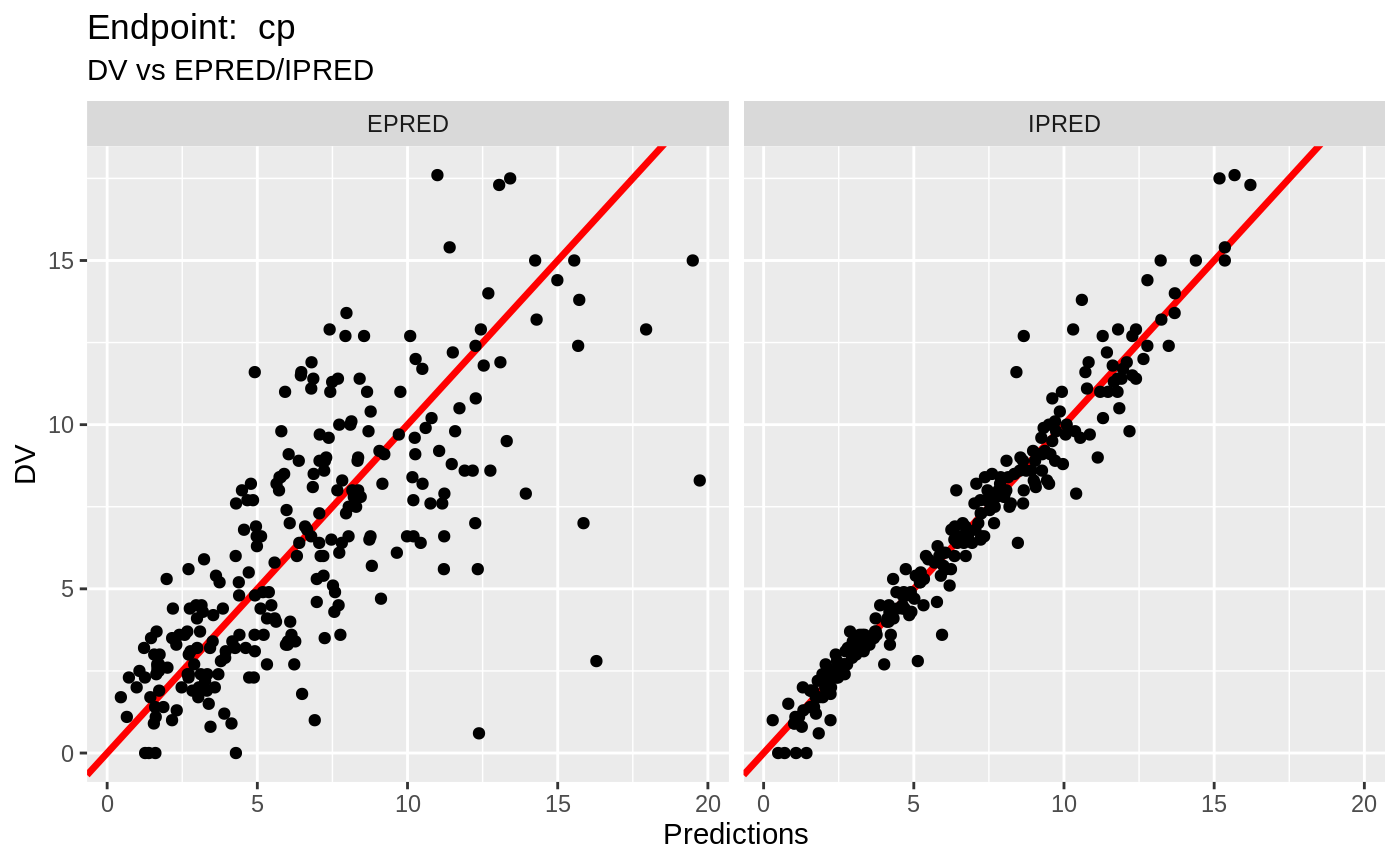
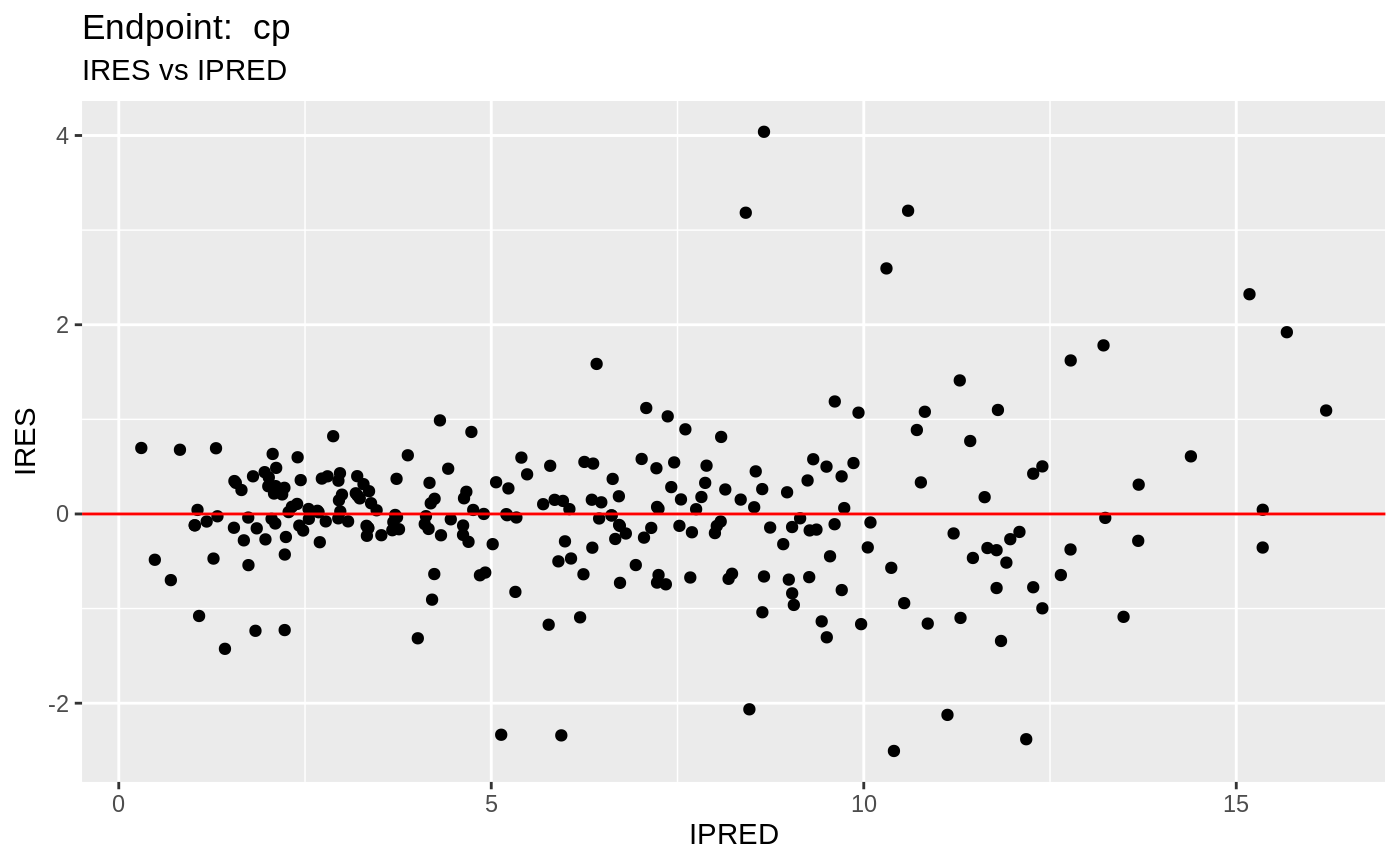
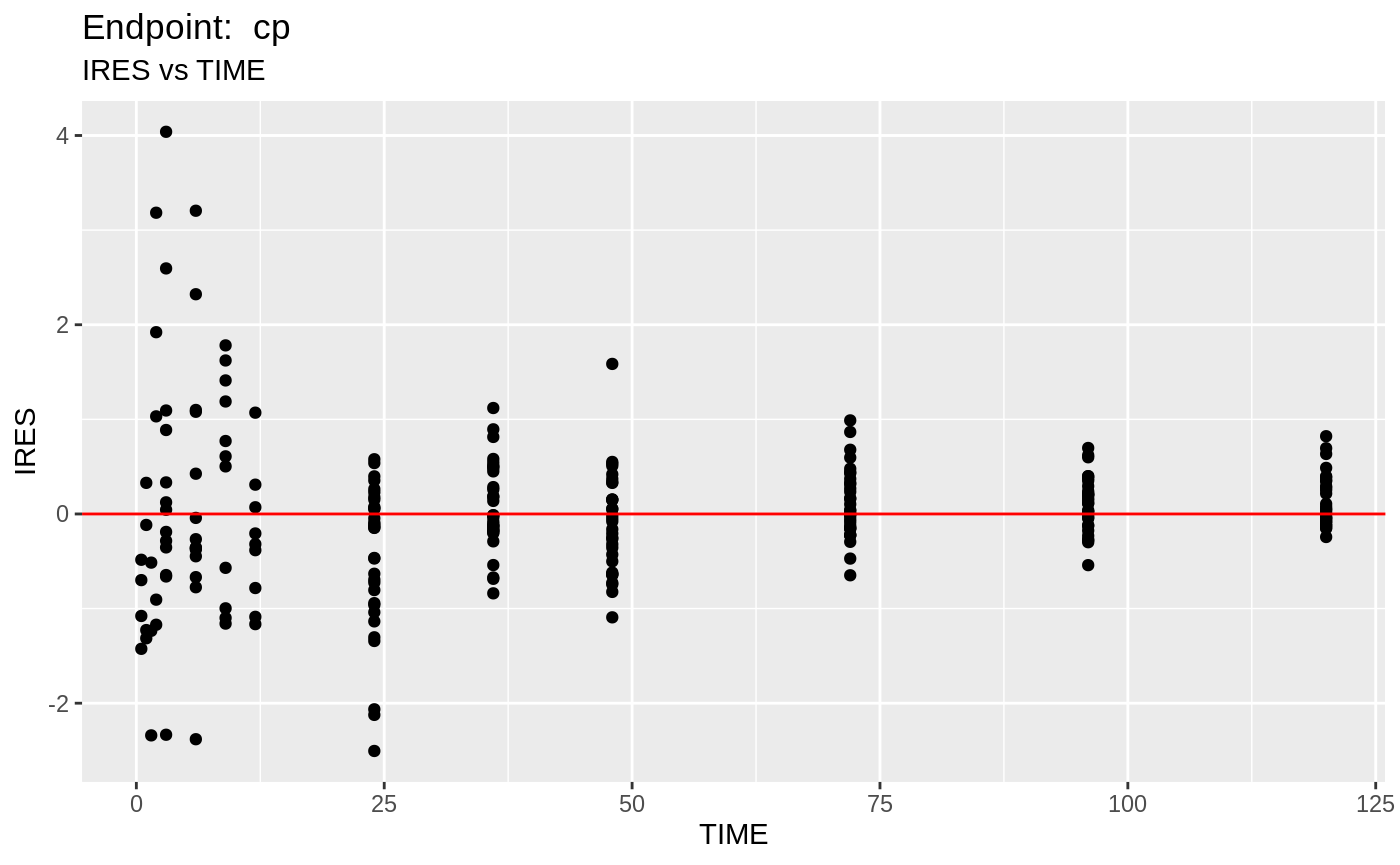
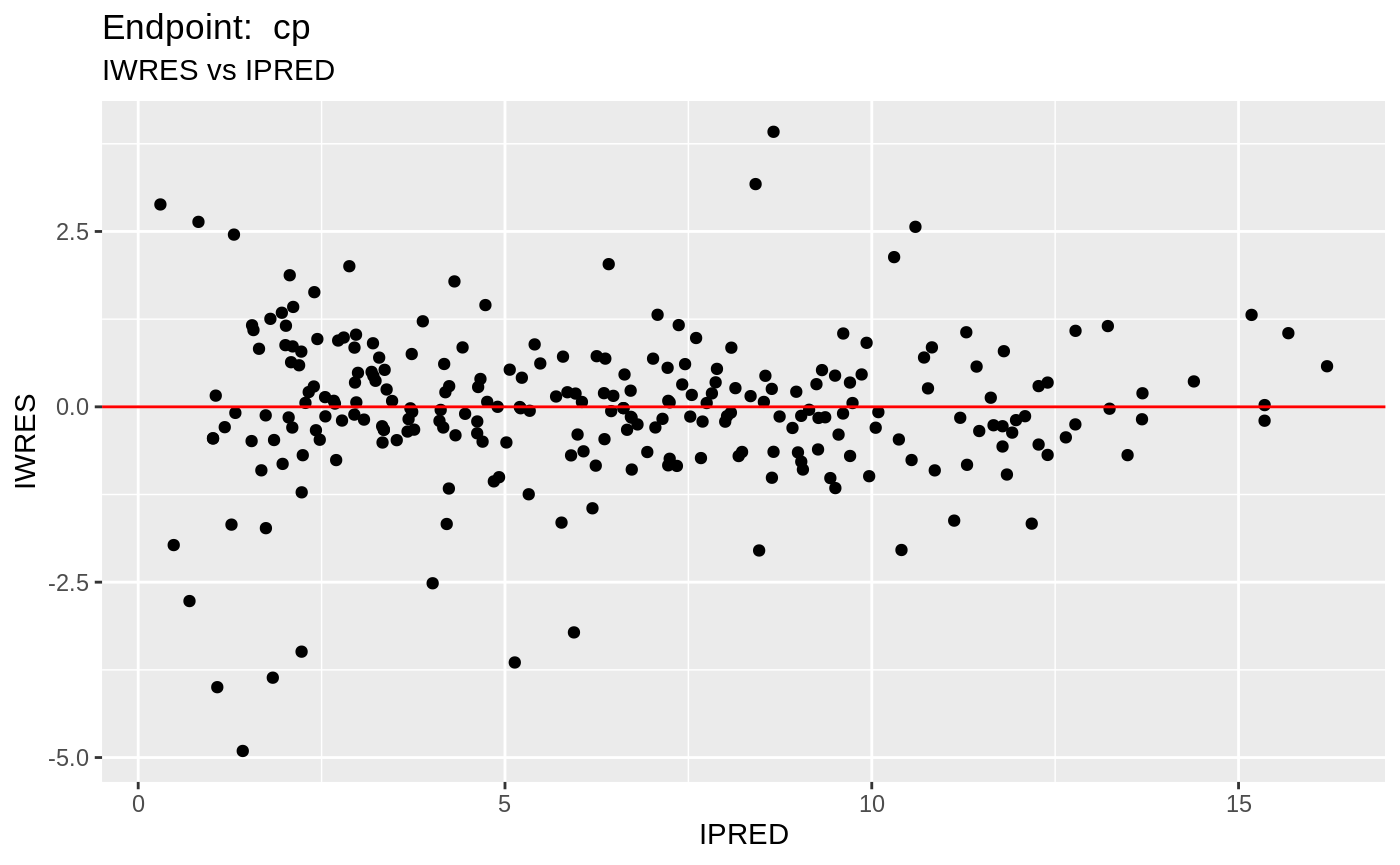
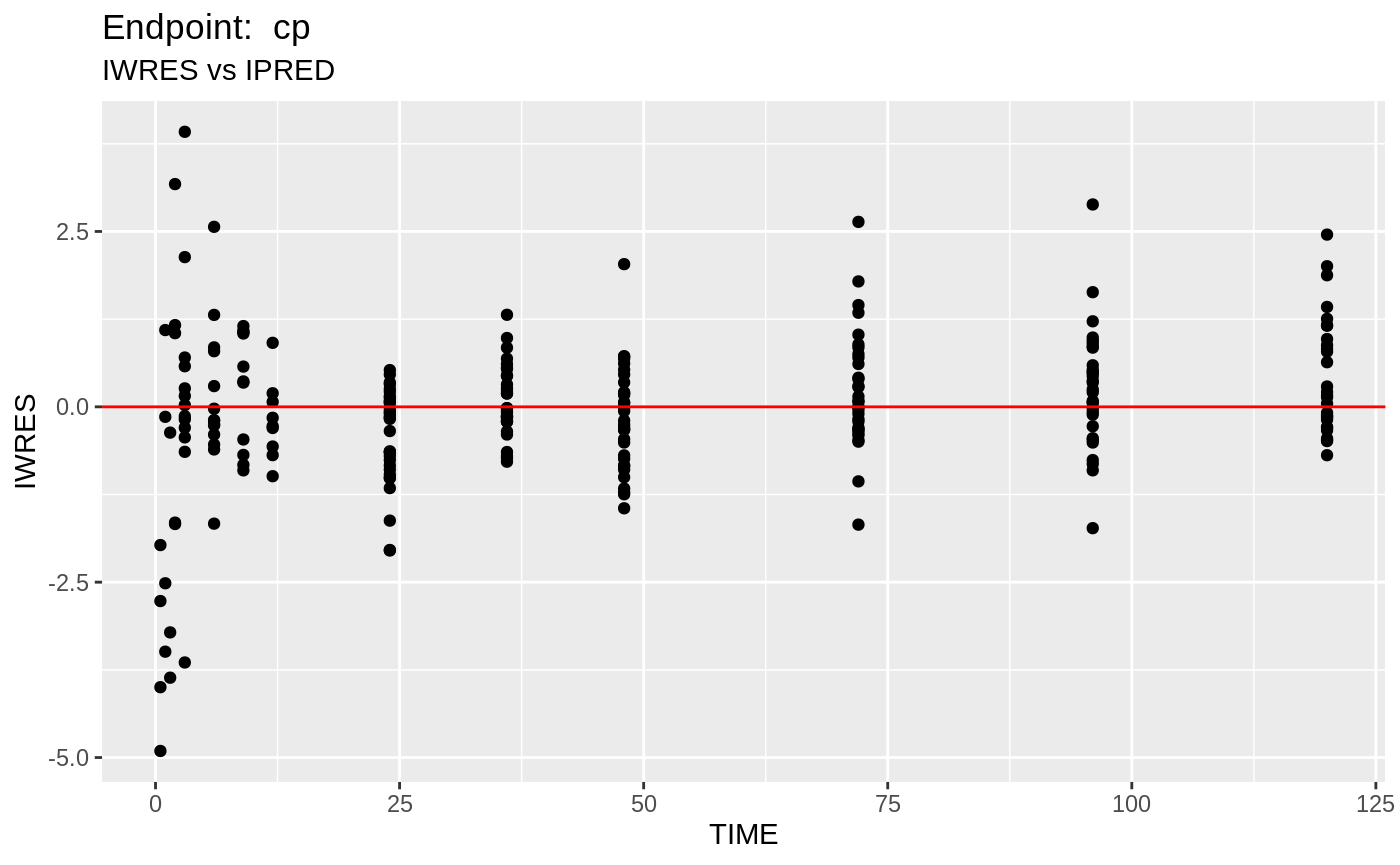
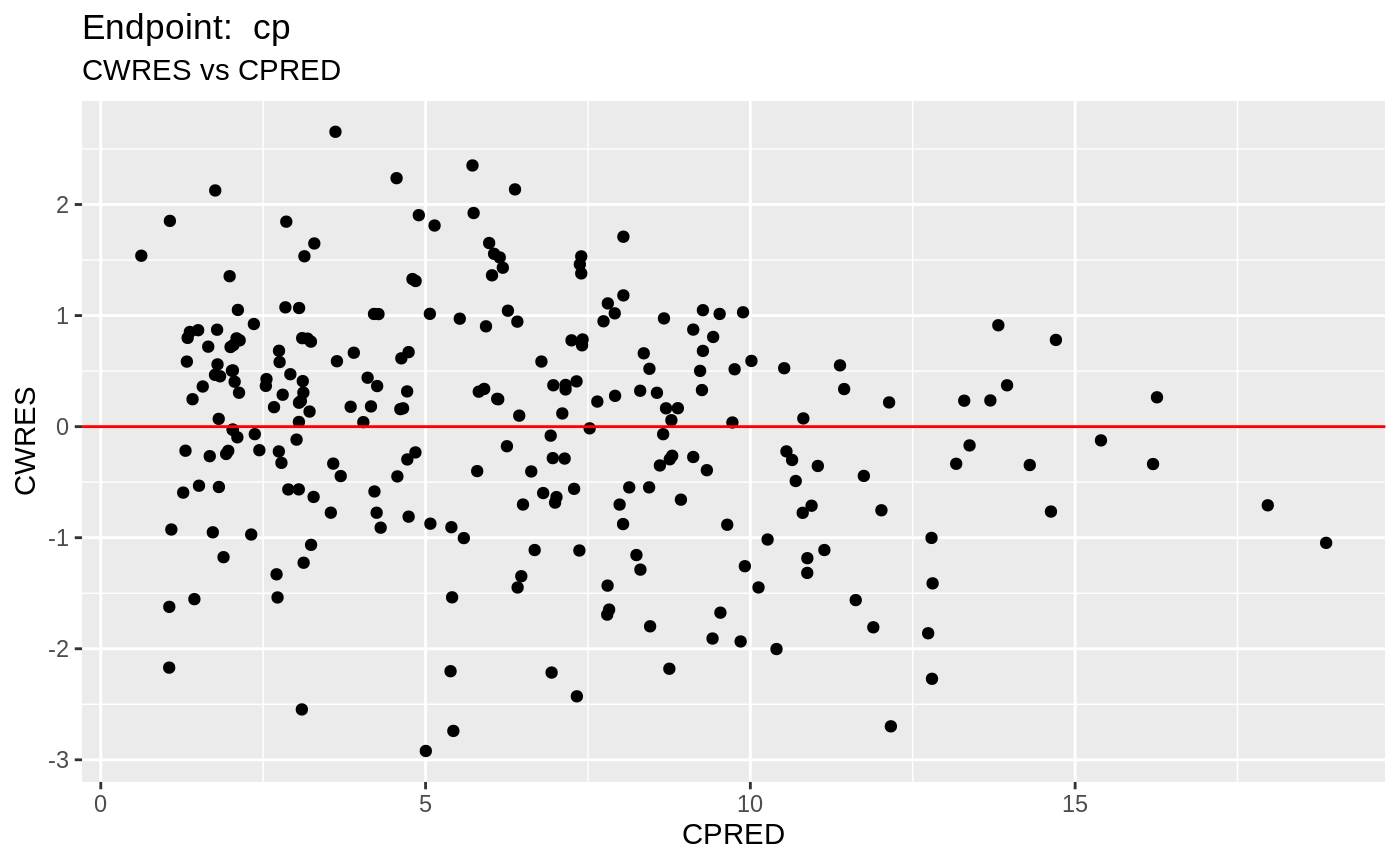
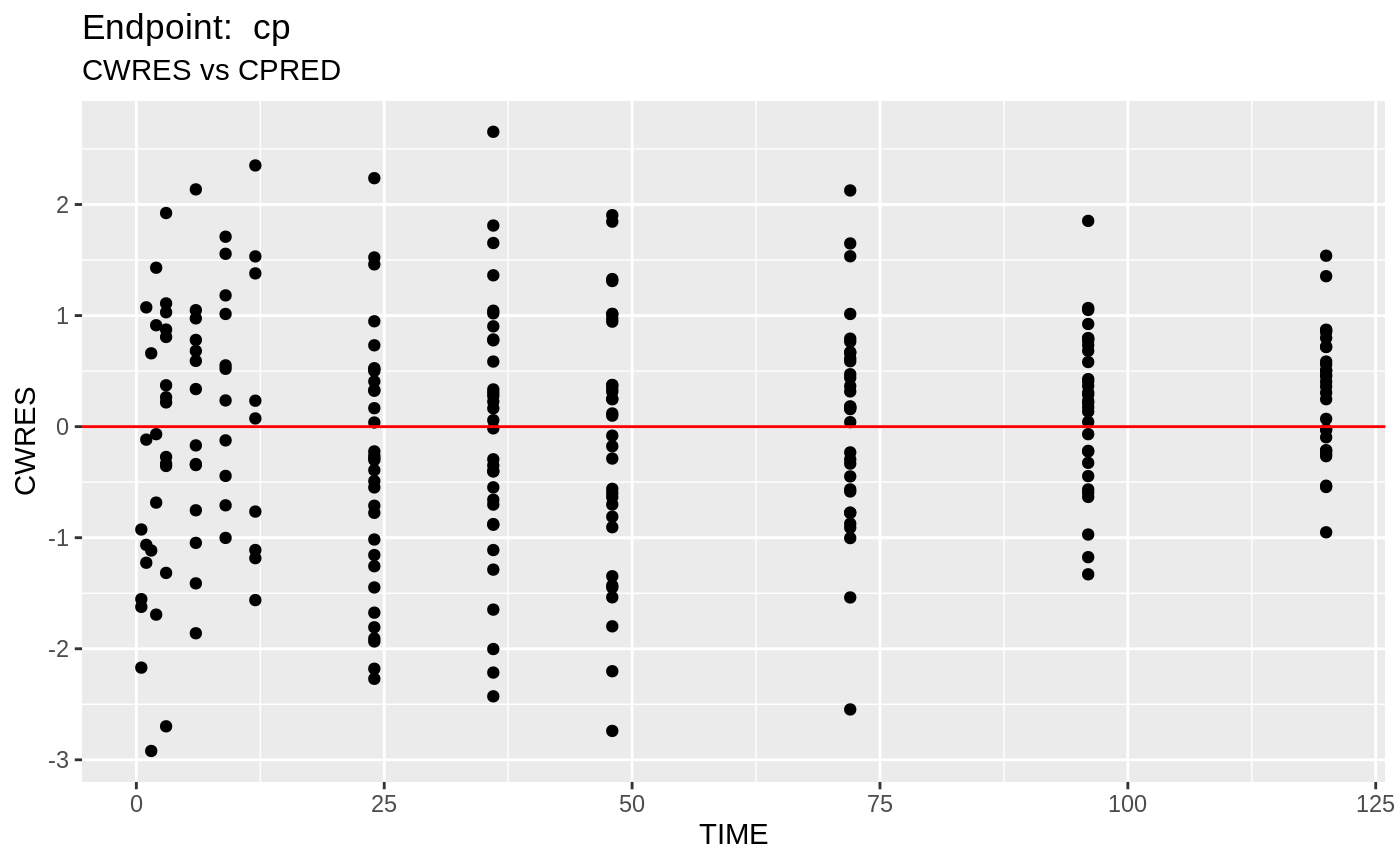
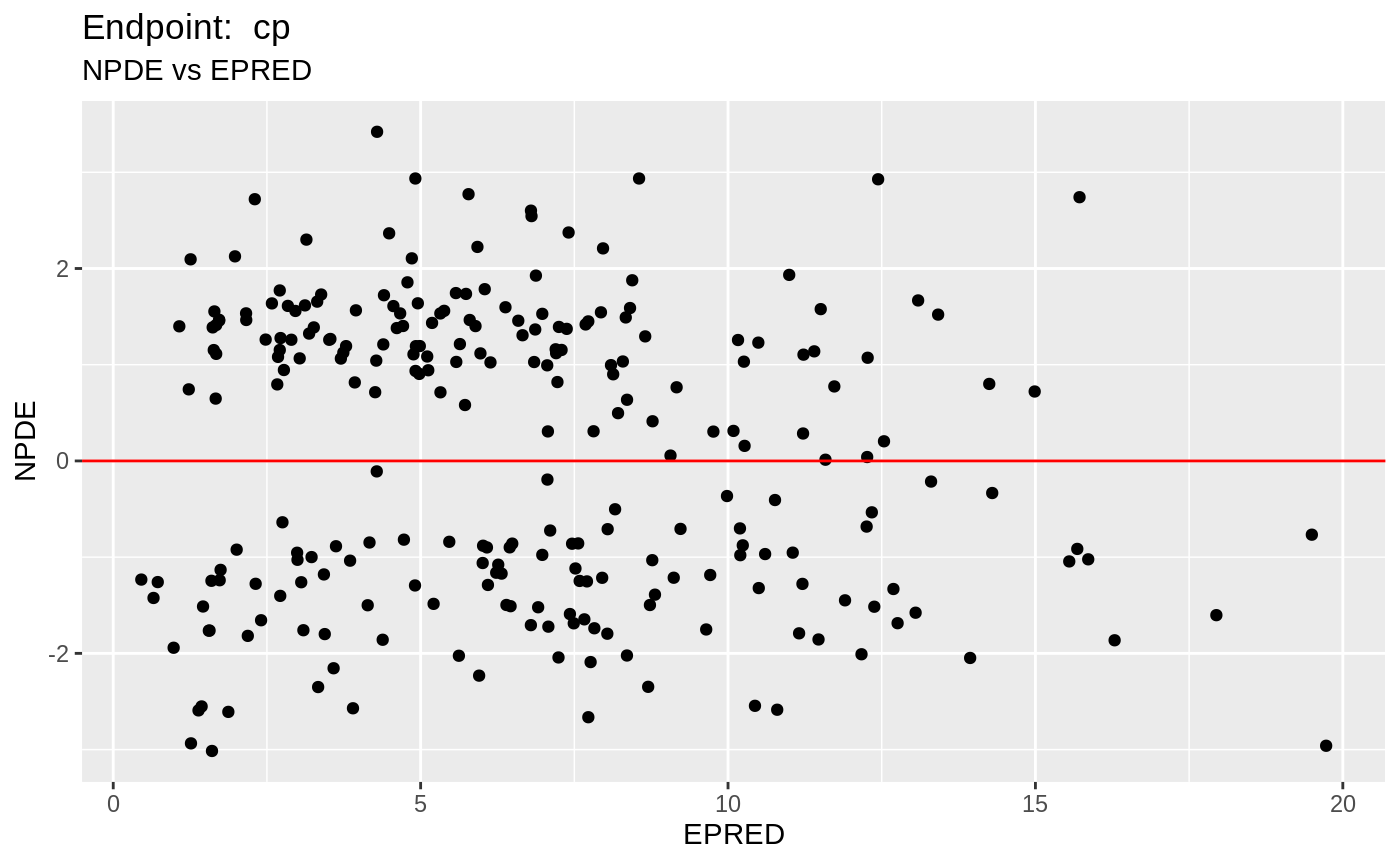
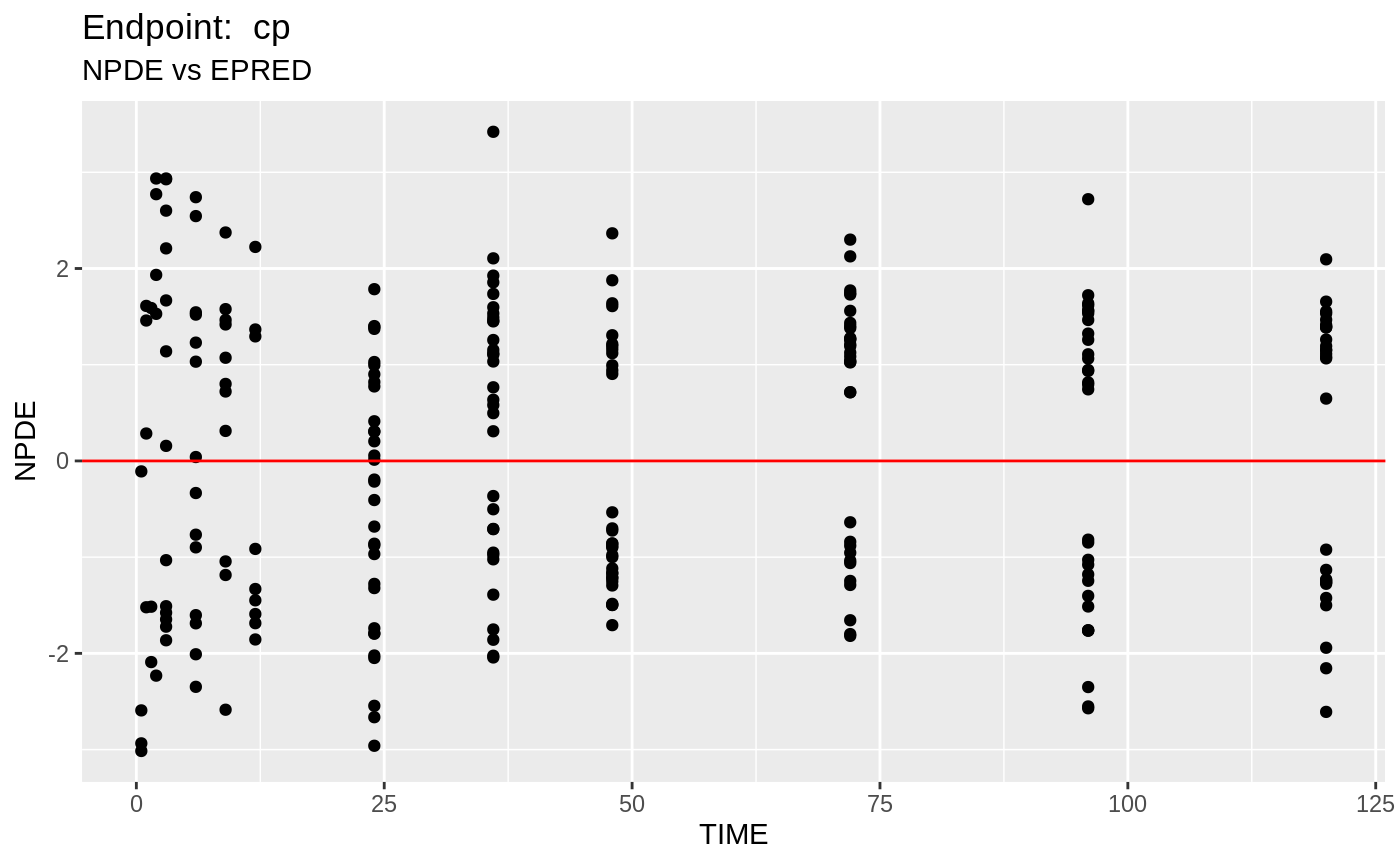
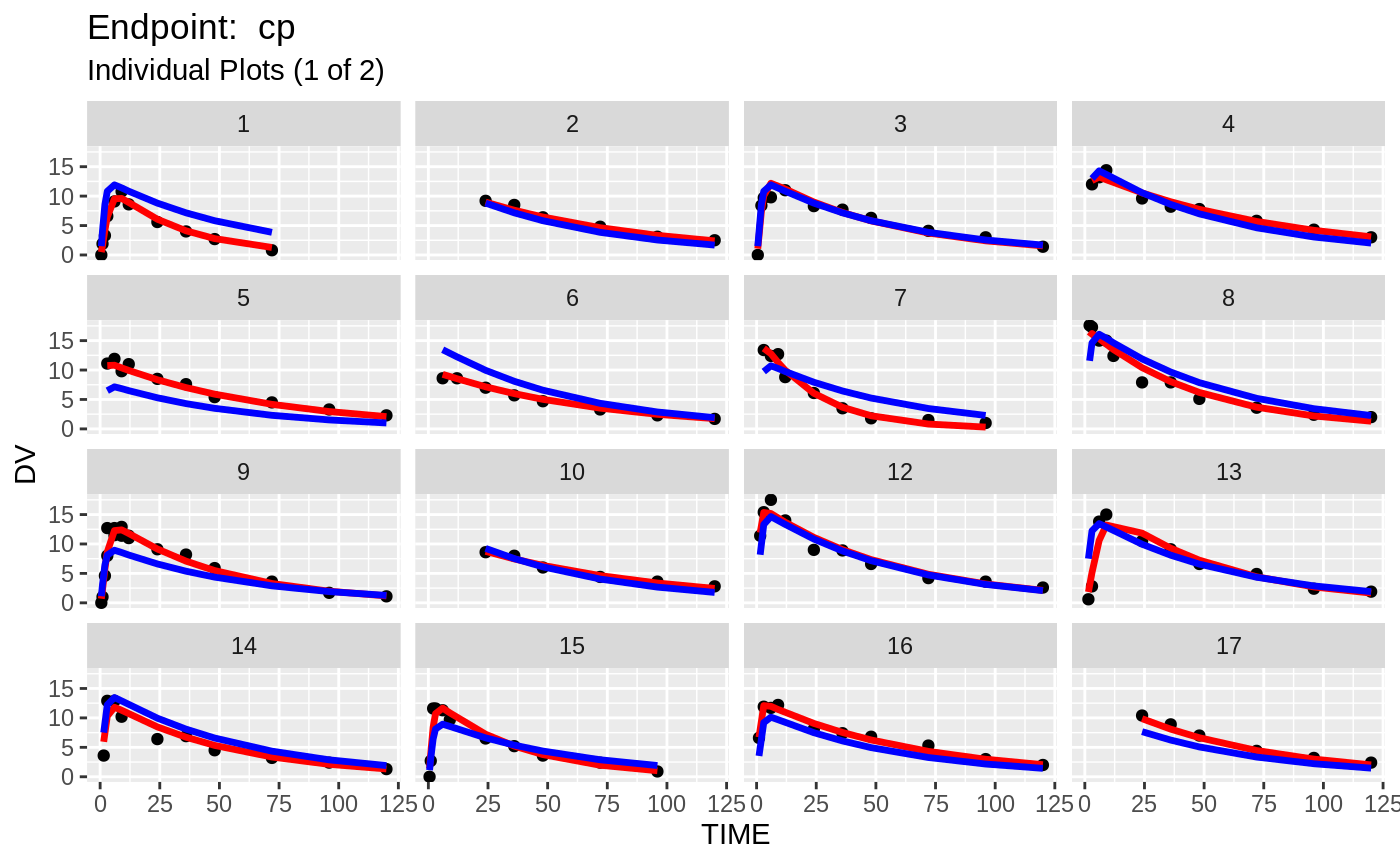
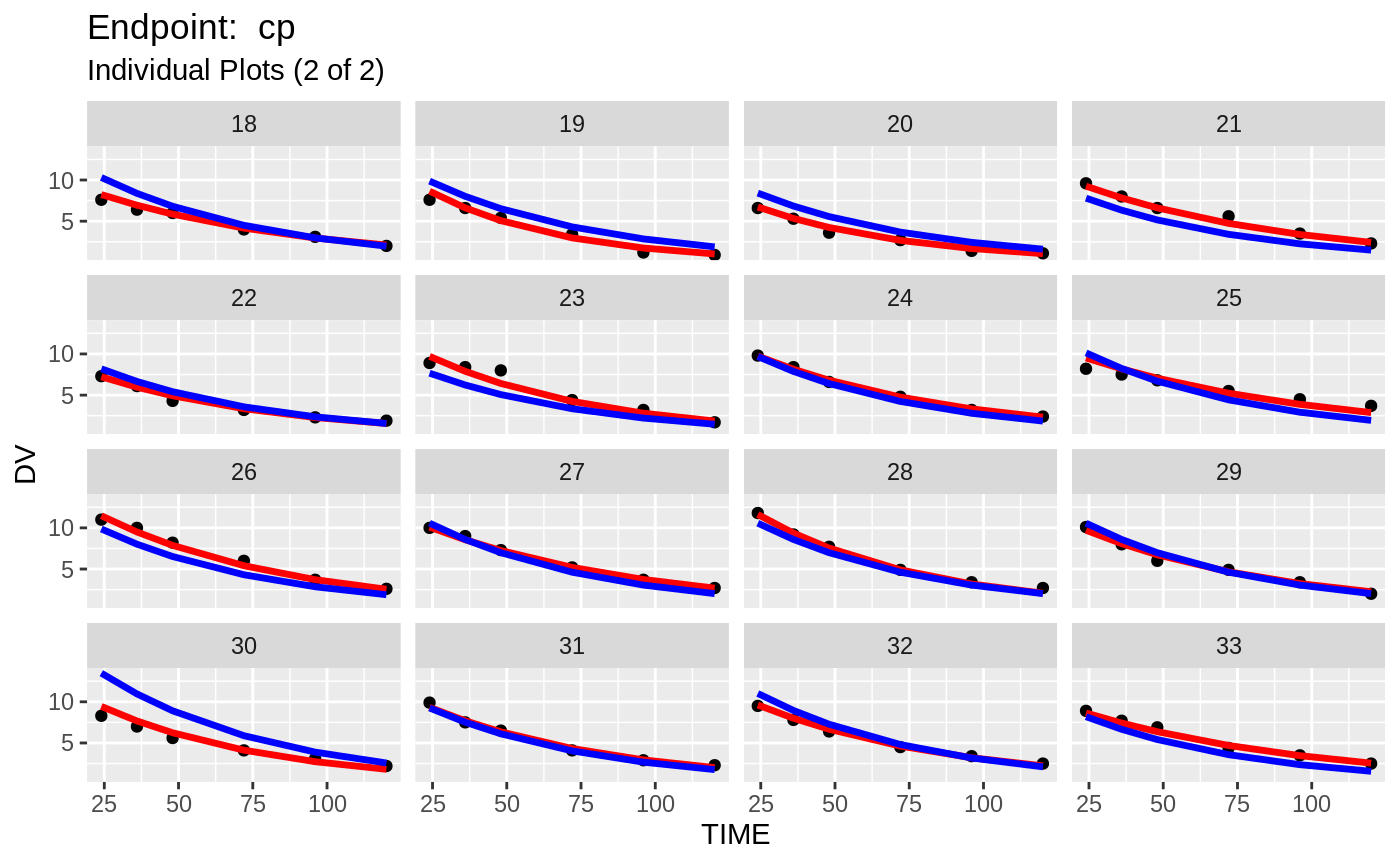
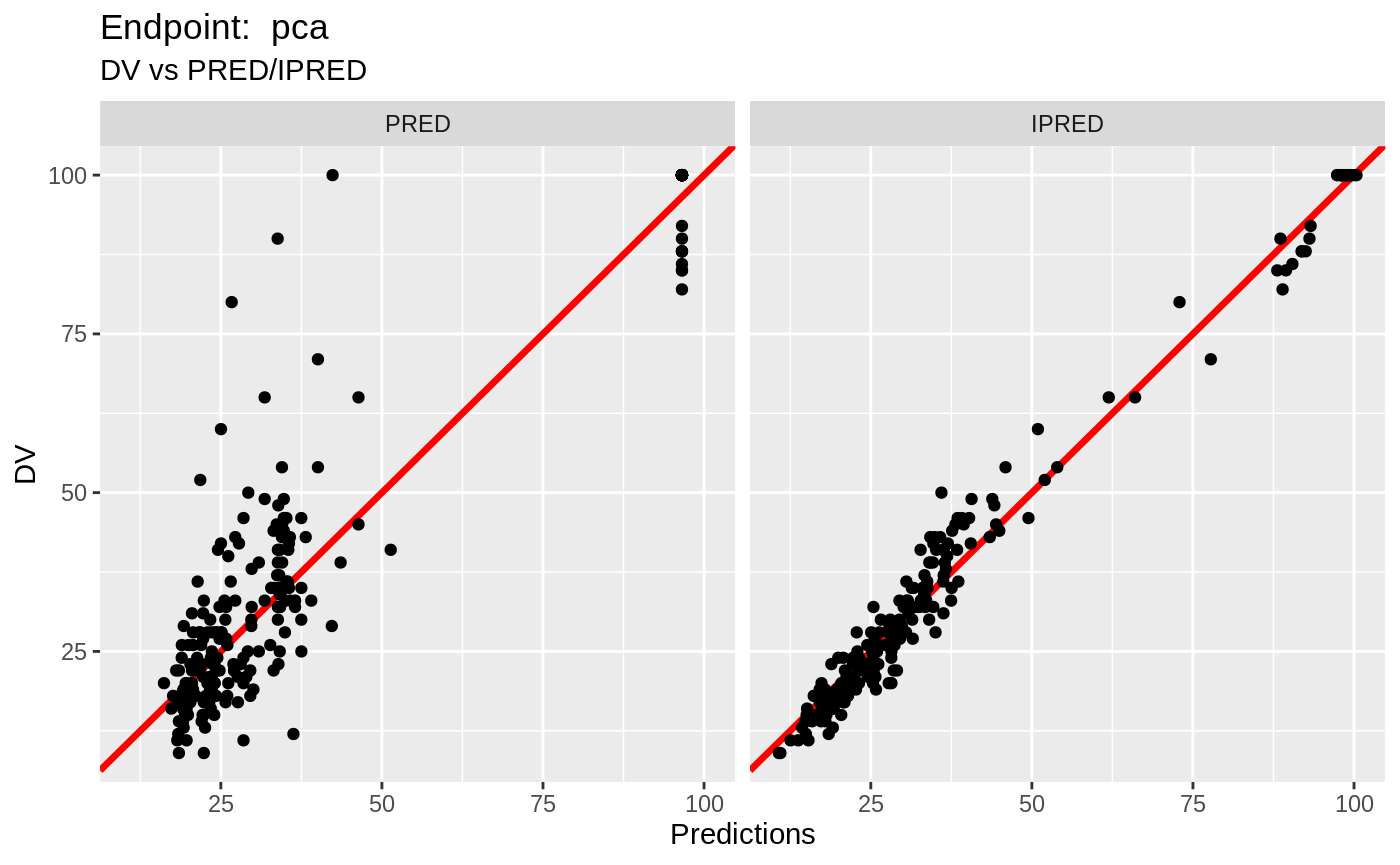
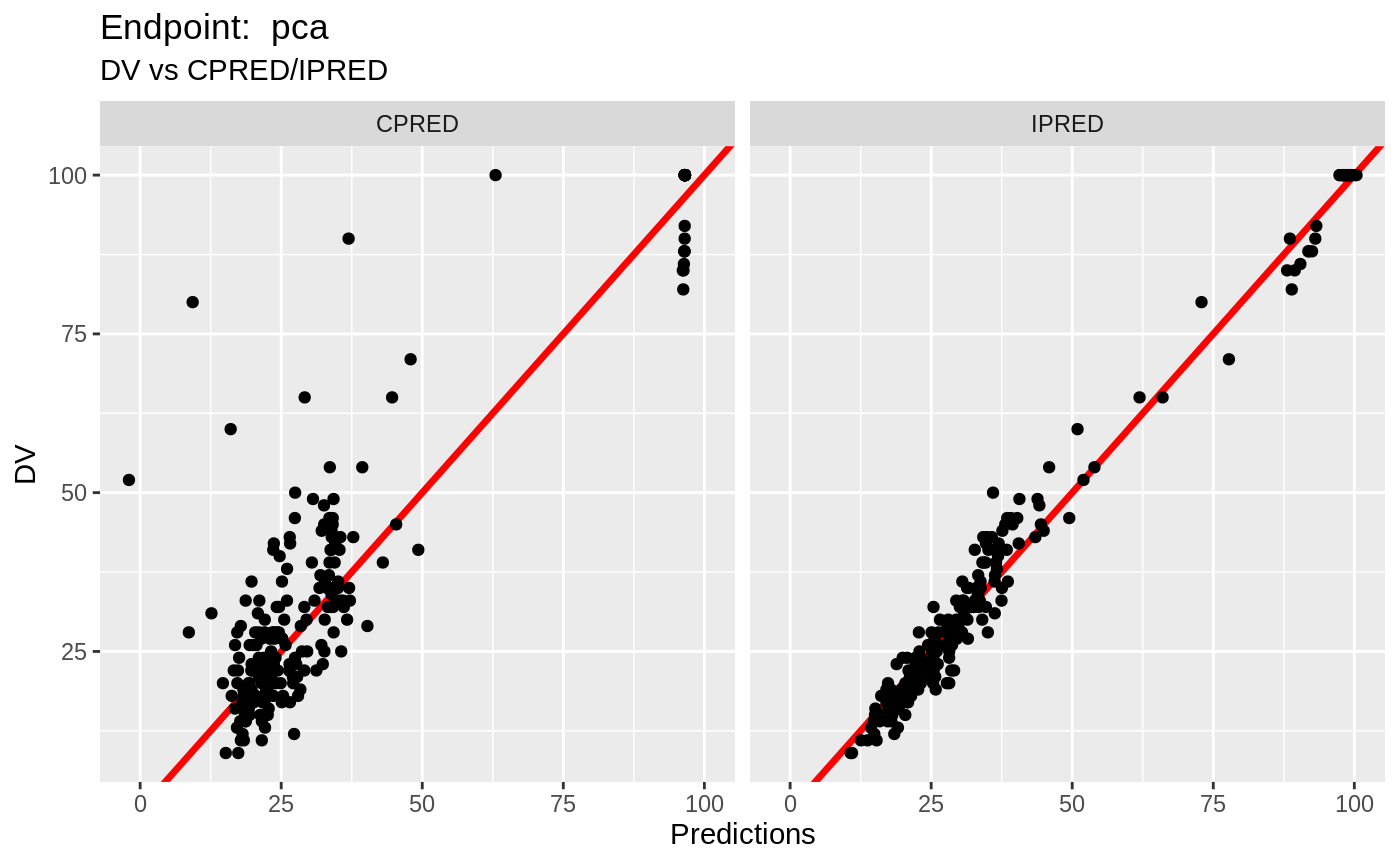
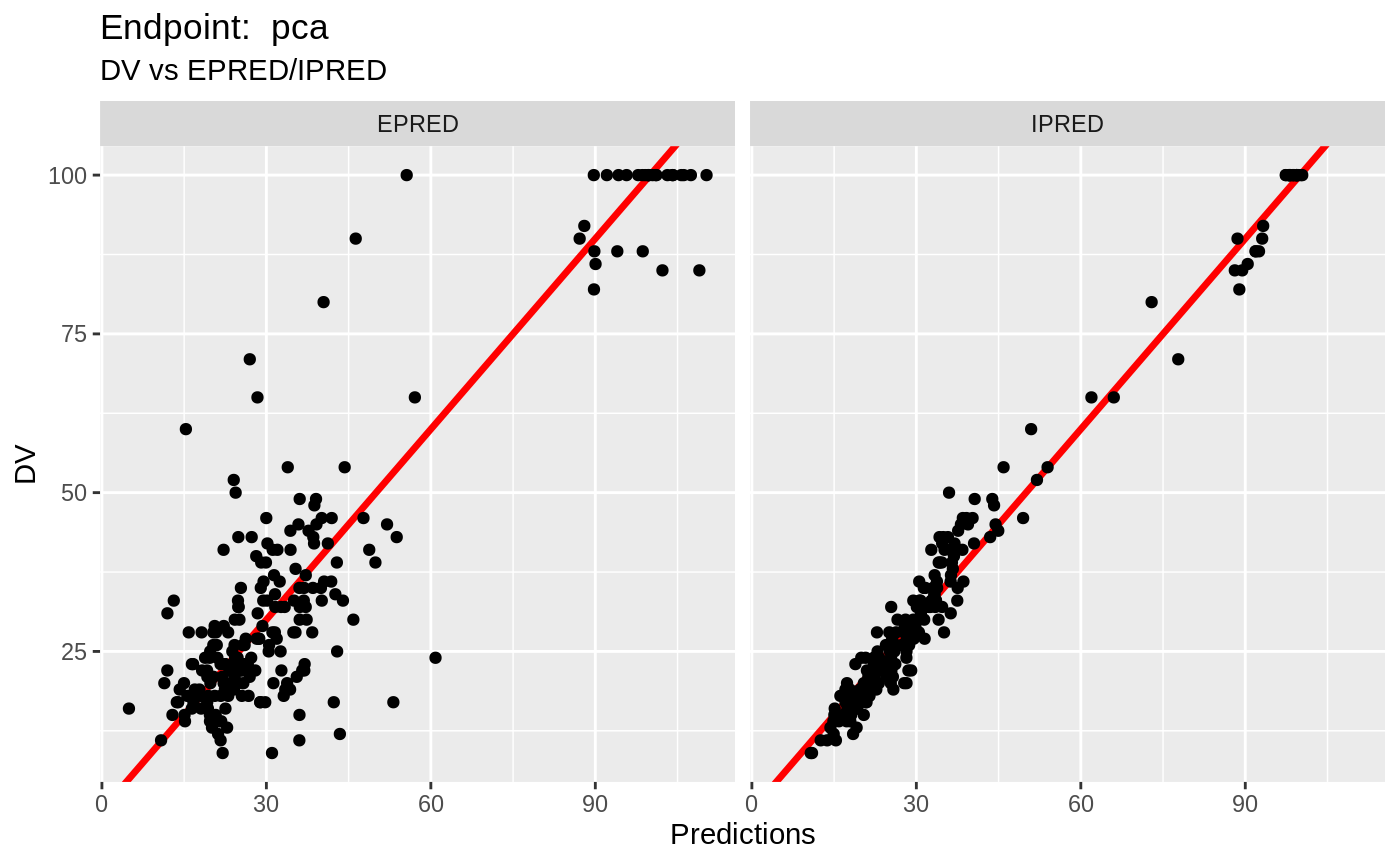
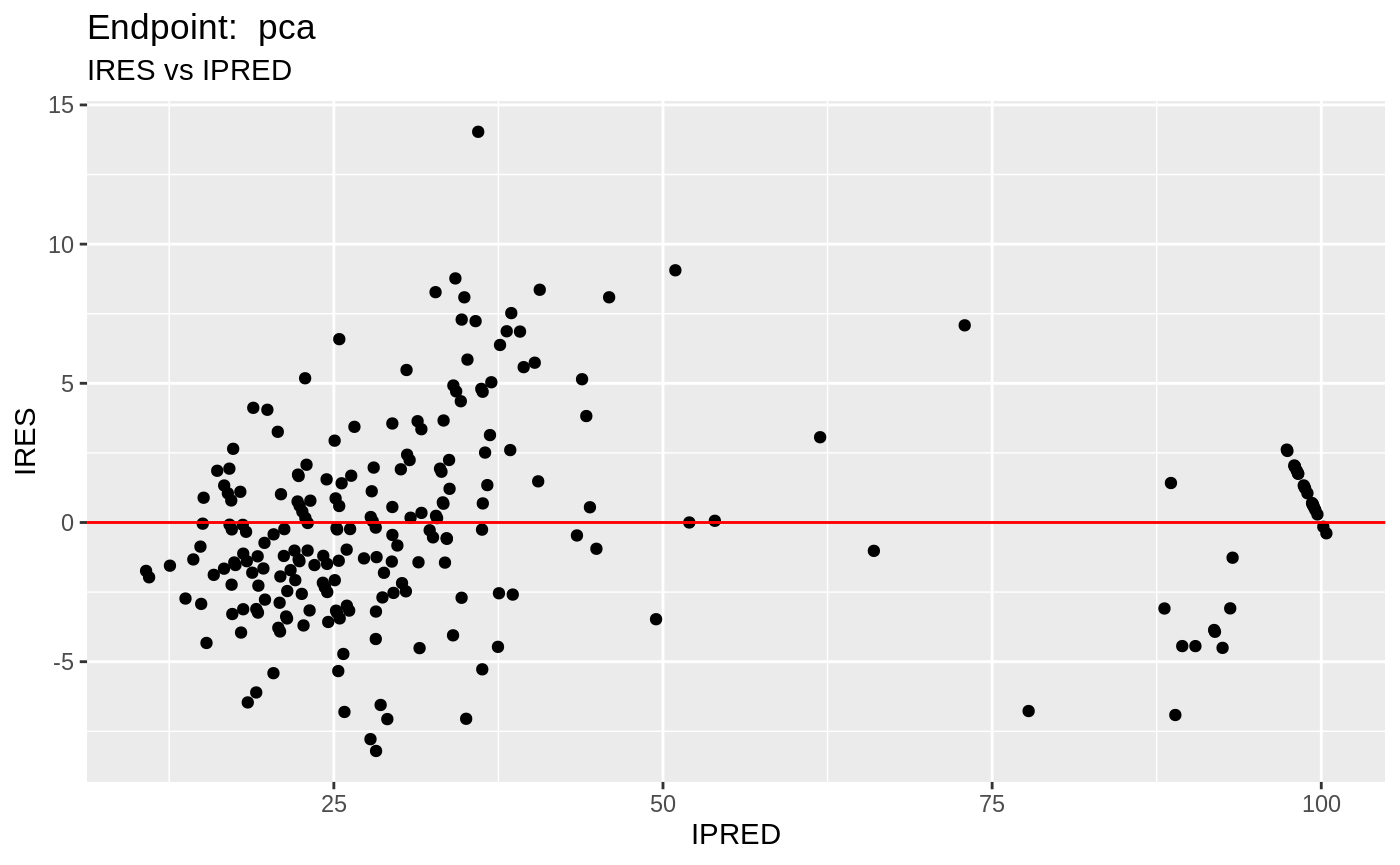
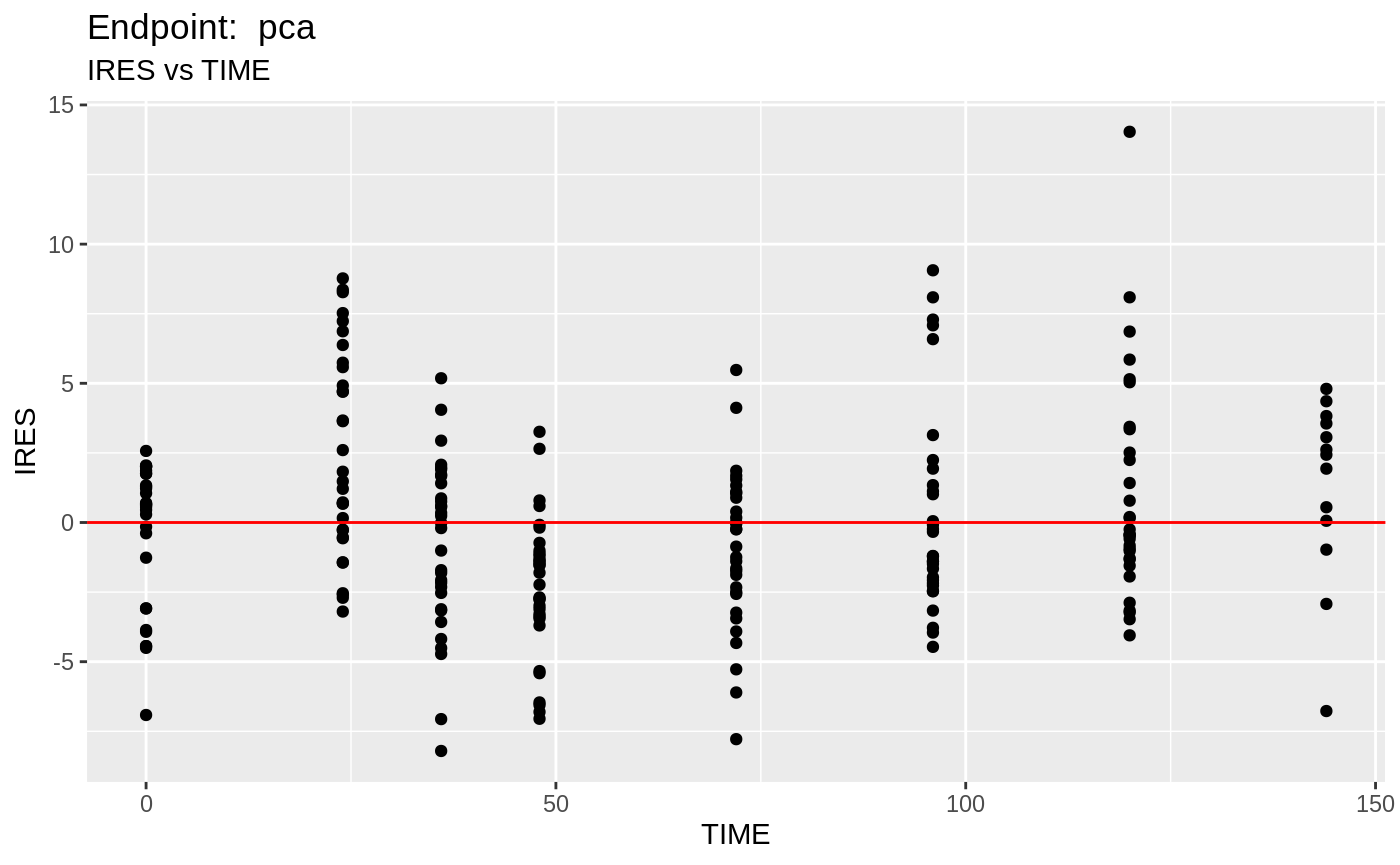
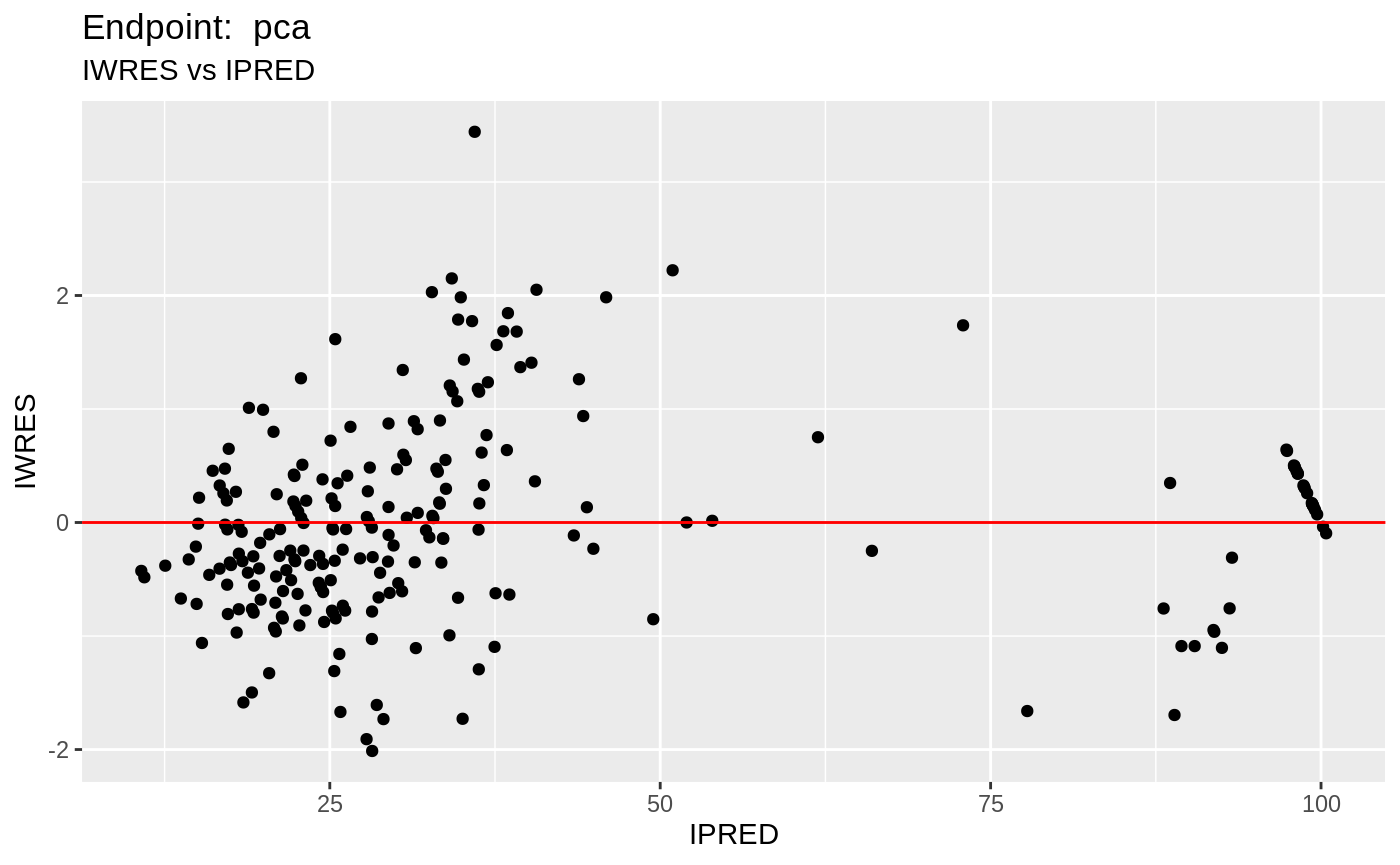
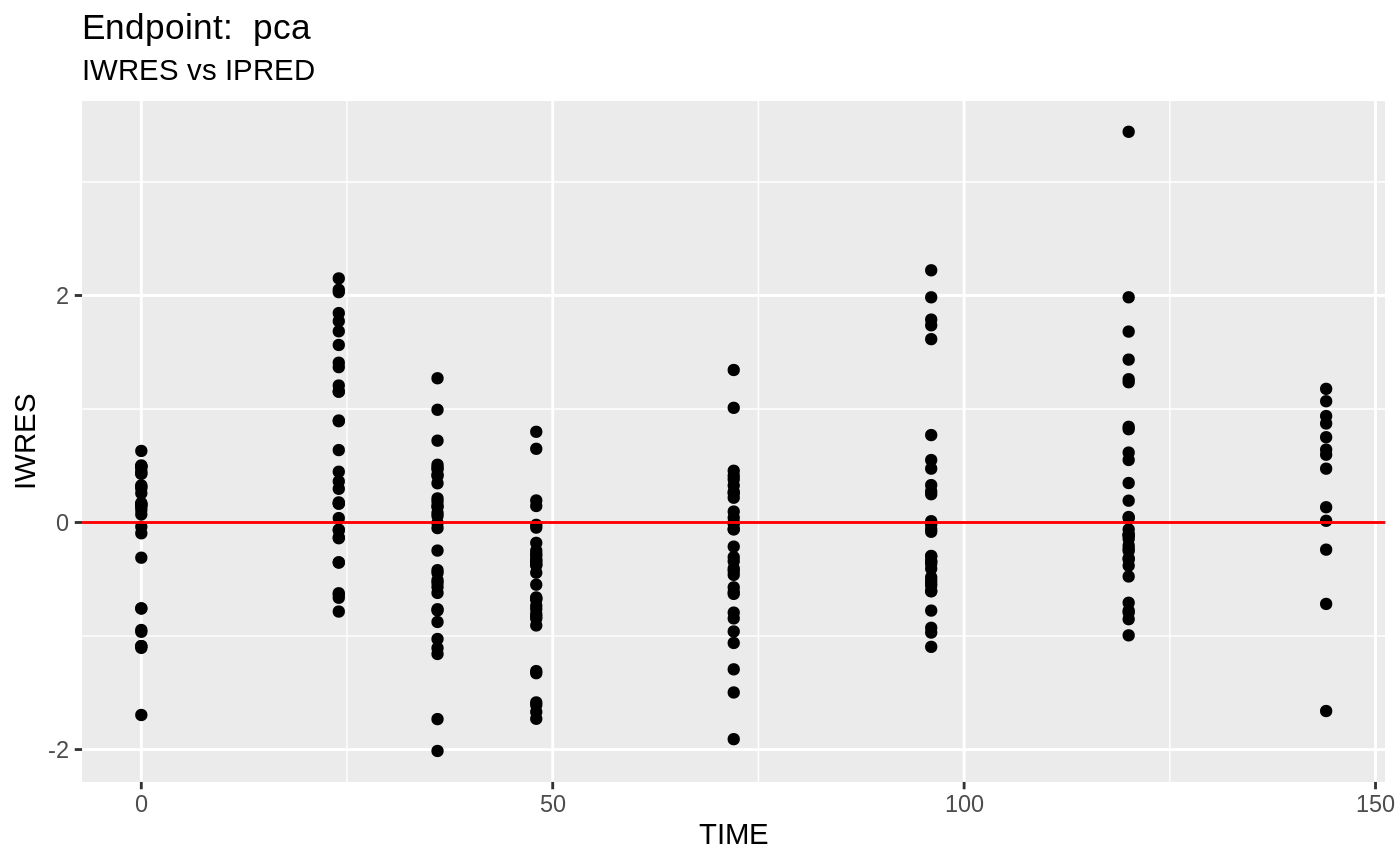
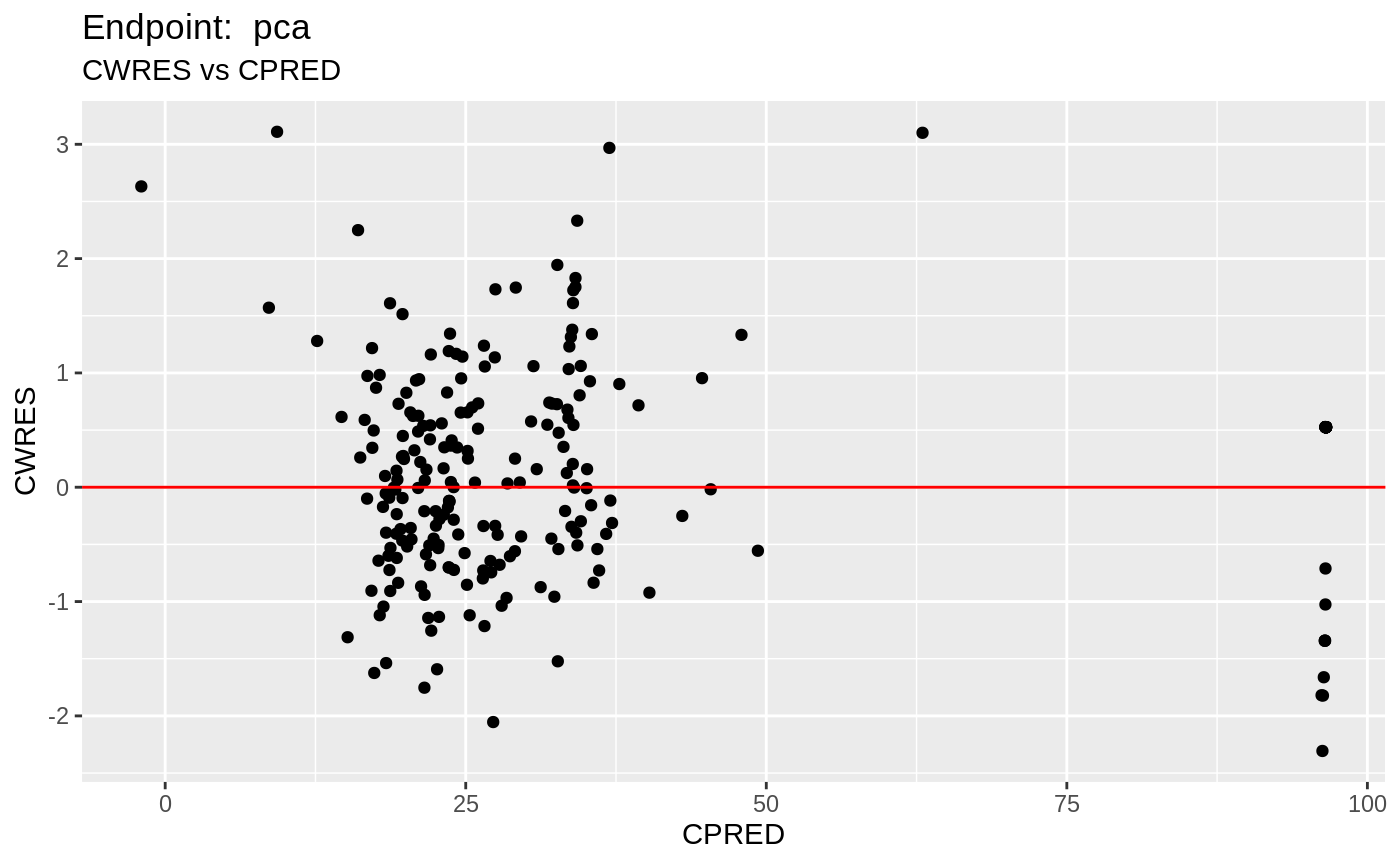
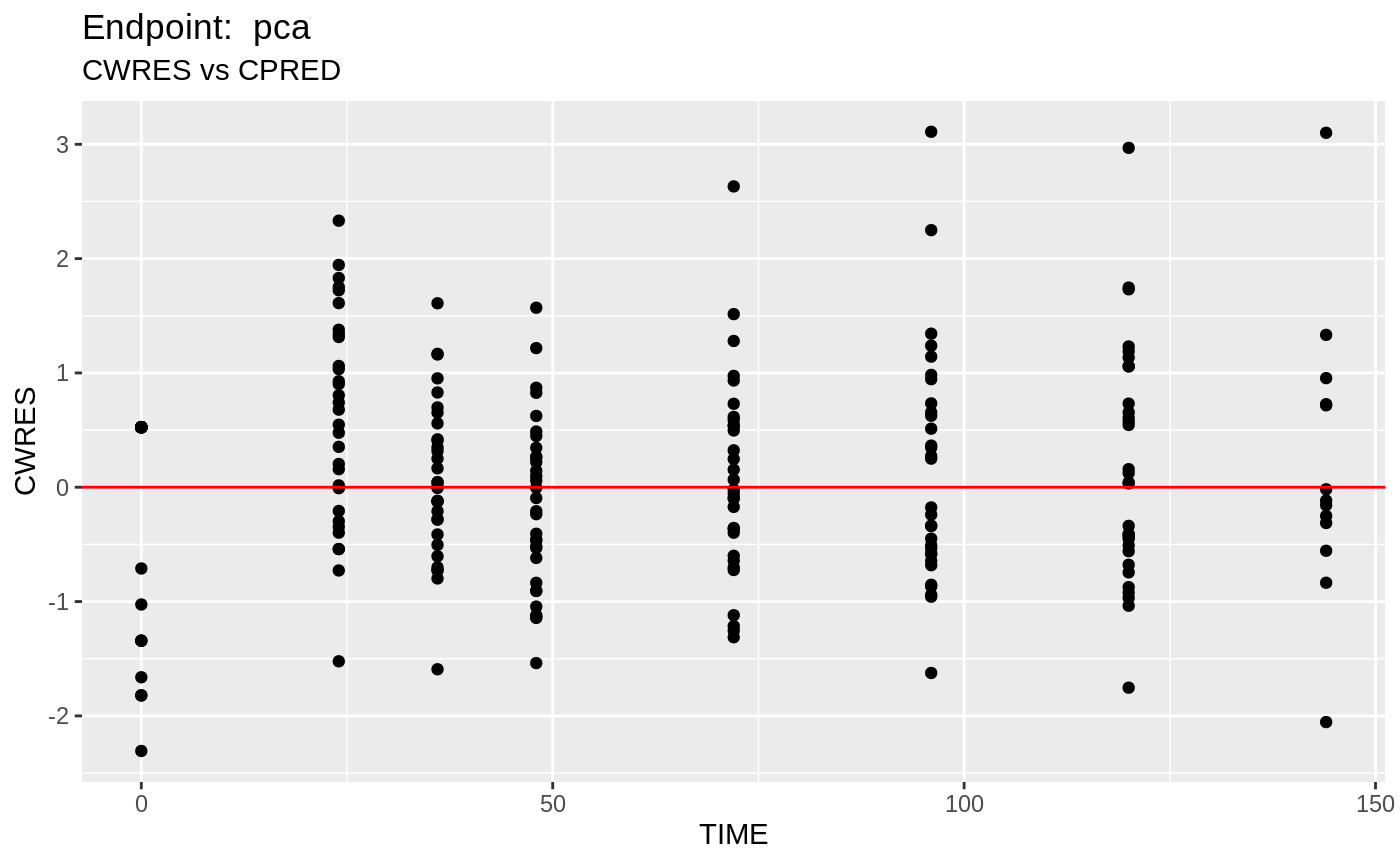
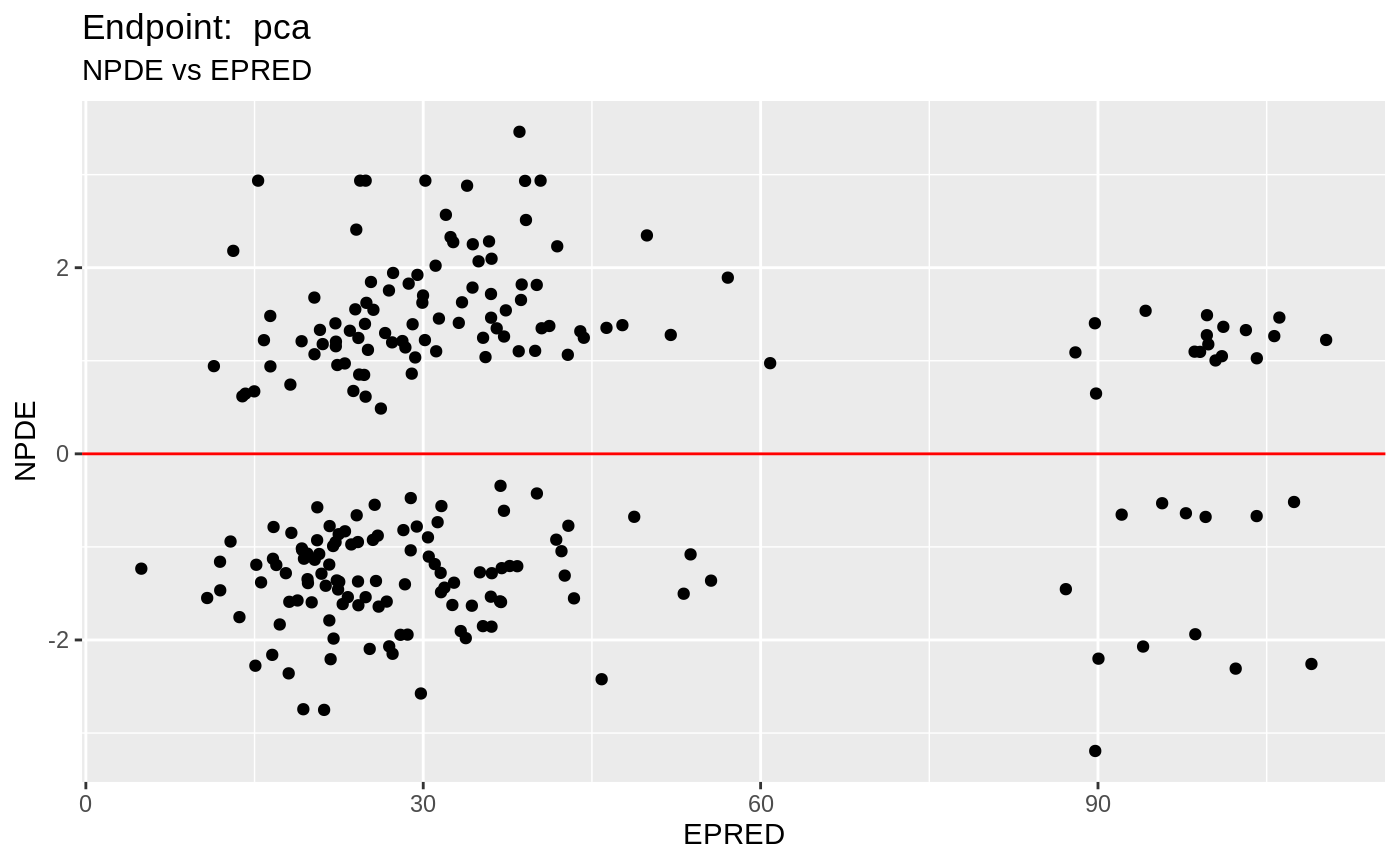
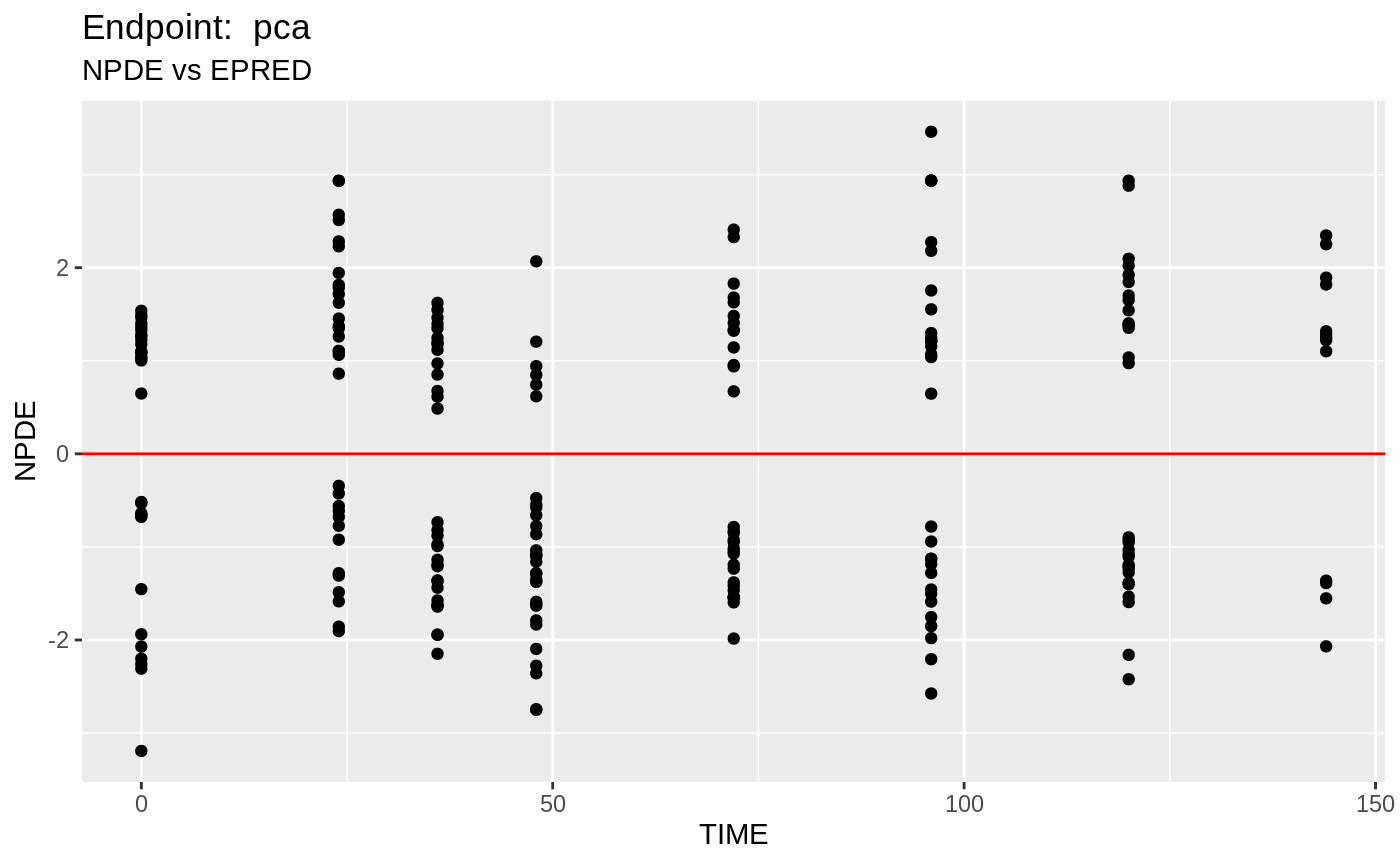
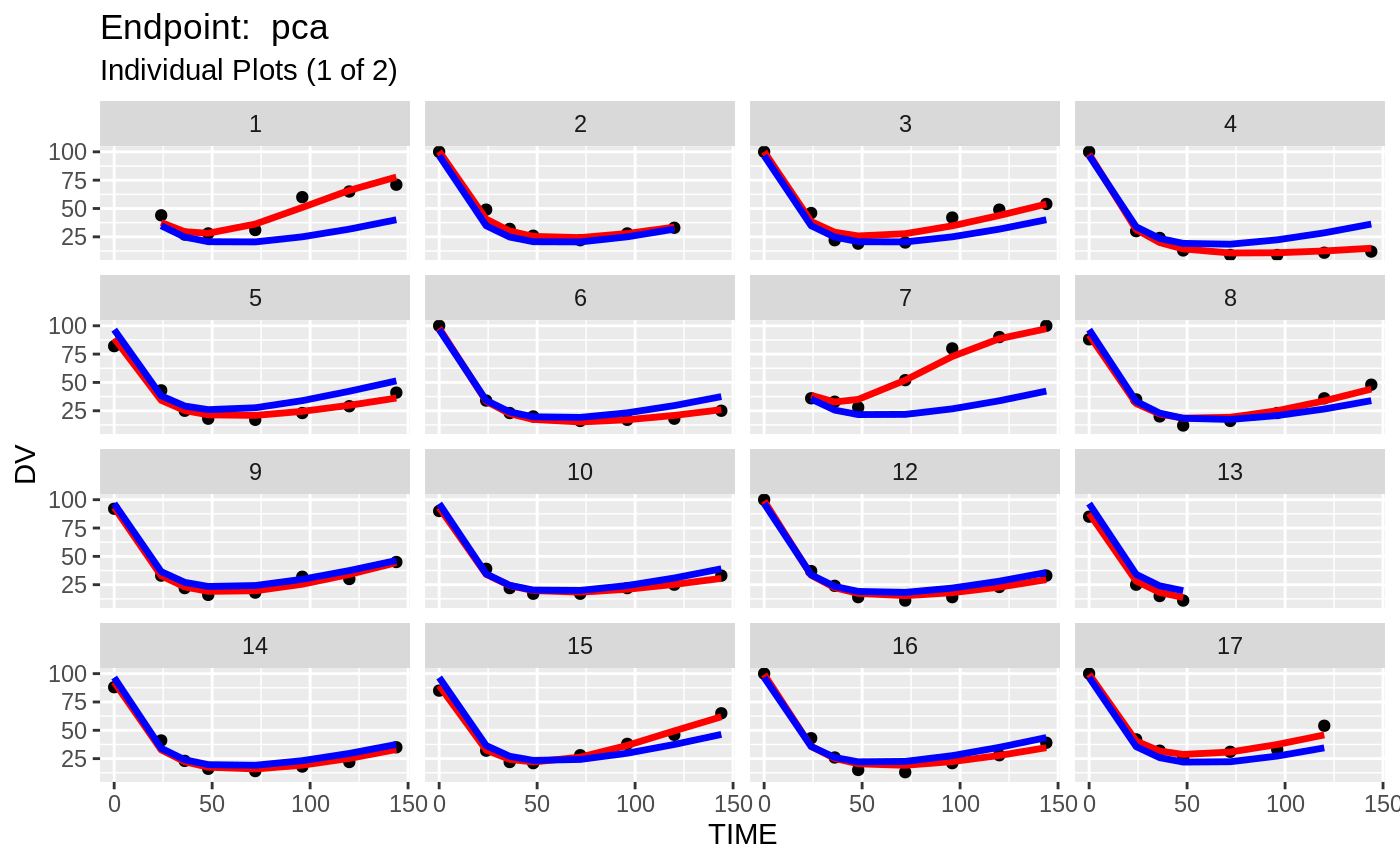
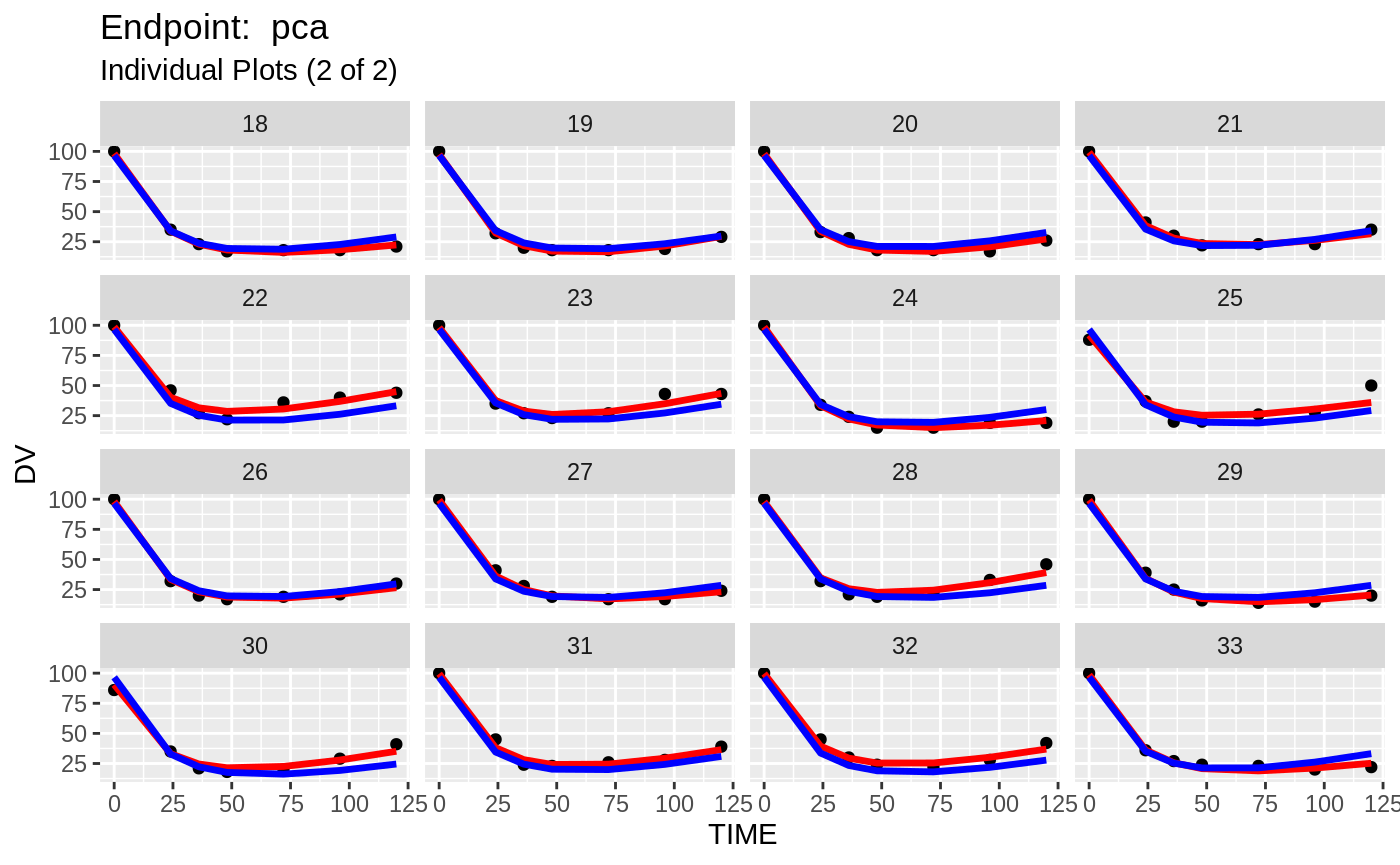
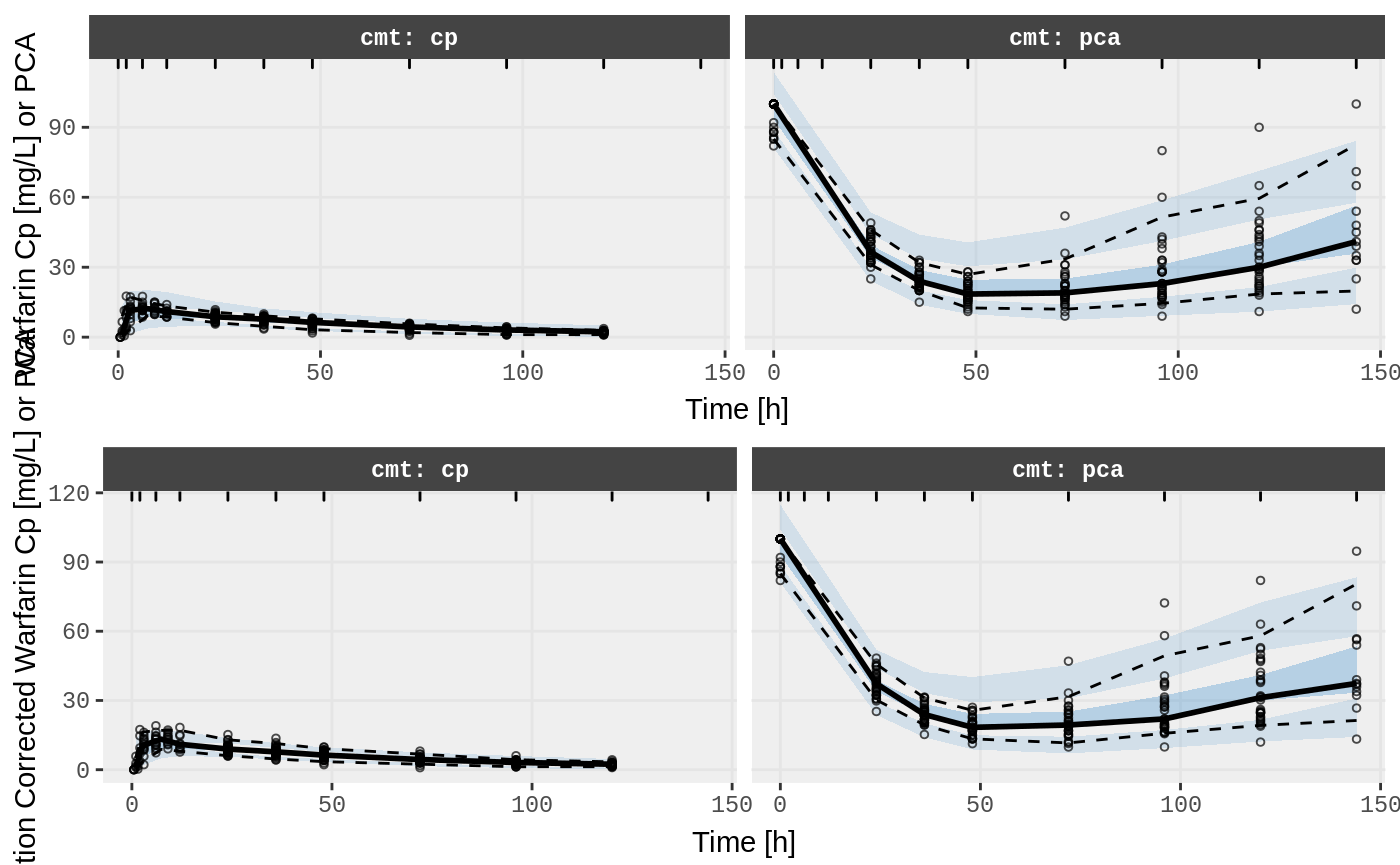
v1s <- nlmixr::vpc(fit.TOS, show=list(obs_dv=T), scales="free_y") +
ylab("Warfarin Cp [mg/L] or PCA") +
xlab("Time [h]");
v2s <- nlmixr::vpc(fit.TOS, show=list(obs_dv=T), pred_corr = TRUE) +
ylab("Prediction Corrected Warfarin Cp [mg/L] or PCA") +
xlab("Time [h]");
gridExtra::grid.arrange(v1s, v2s)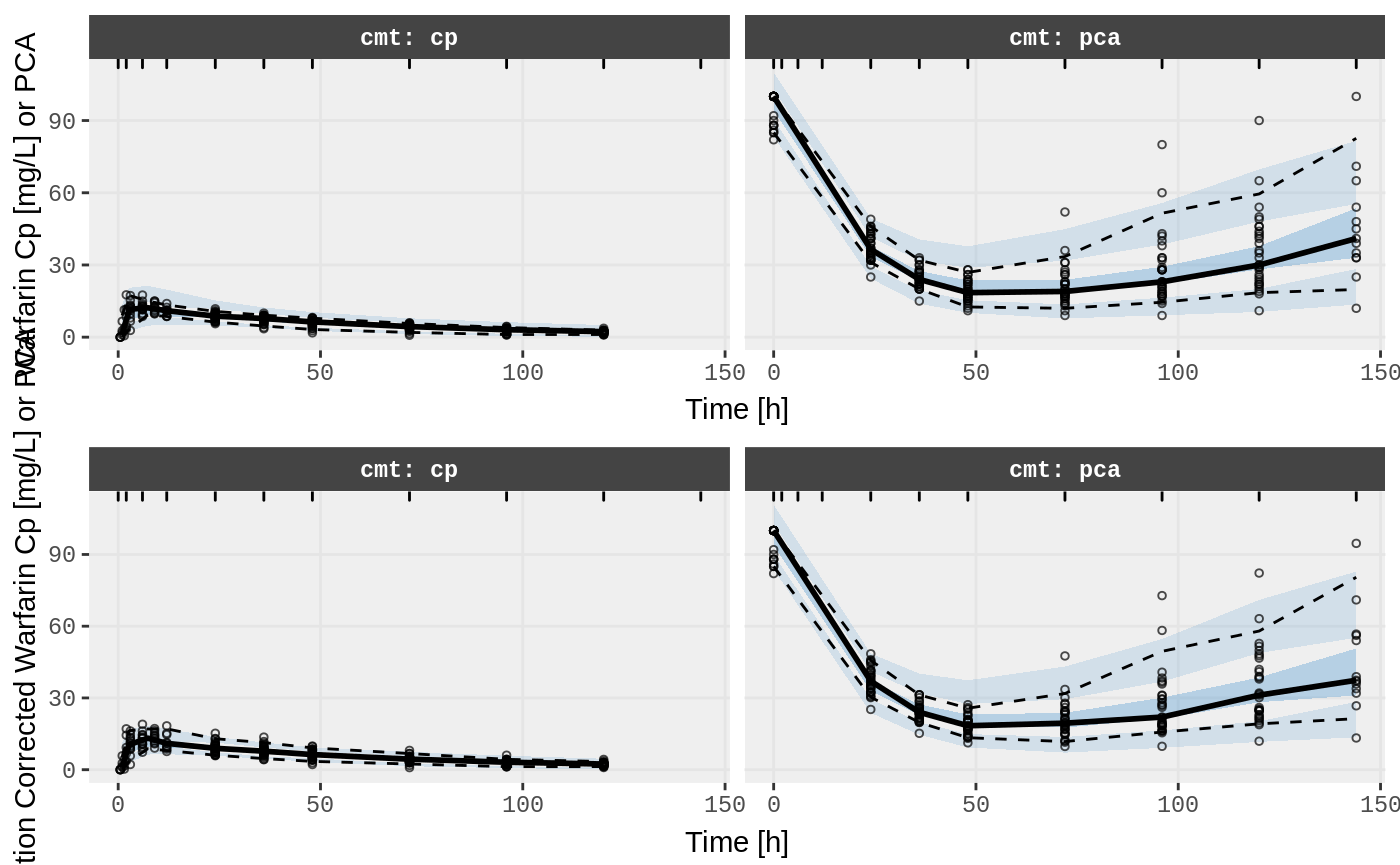
FOCEi fits
## FOCEi fit/vpcs
fit.TOF <- nlmixr(pk.turnover.emax3, warfarin, "focei", control=list(print=0),
table=list(cwres=TRUE, npde=TRUE));FOCEi Diagnostic Plots
print(fit.TOF)
#> ── nlmixr FOCE[31;1mi[0m (outer: nlminb) fit ───────────────────────────────────────
#> OBJF AIC BIC Log-likelihood Condition Number
#> FOCEi 1372.972 2298.666 2378.086 -1130.333 4175.2
#>
#> ── Time (sec; $time): ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> setup optimize covariance table npde other
#> elapsed 0.324265 46.0624 46.0624 0.023 0.593 220.7769
#>
#> ── Population Parameters ($parFixed or $parFixedDf): ──────────────────────
#> Est. SE %RSE Back-transformed(95%CI) BSV(CV%) Shrink(SD)%
#> tktr 0.074 0.164 222 1.08 (0.78, 1.49) 106. 62.7%
#> tka 0.129 0.145 112 1.14 (0.856, 1.51) 110. 62.5%
#> tcl -2.01 0.0387 1.92 0.134 (0.124, 0.145) 27.9 -0.302%
#> tv 2.07 0.0323 1.56 7.91 (7.43, 8.43) 21.7 4.54%
#> prop.err 0.129 0.129
#> pkadd.err 0.239 0.239
#> poplogit 3.84 0.245 6.38 46.5 (28.8, 75.1) 51.0 89.5%
#> tec50 0.166 0.0624 37.7 1.18 (1.04, 1.33) 49.4 6.95%
#> tkout -2.91 0.0339 1.16 0.0542 (0.0507, 0.0579) 11.0 31.4%
#> te0 4.57 0.0134 0.292 96.4 (94, 99) 7.08 26.6%
#> pdadd.err 3.87 3.87
#>
#> Covariance Type ($covMethod): r,s
#> No correlations in between subject variability (BSV) matrix
#> Full BSV covariance ($omega) or correlation ($omegaR; diagonals=SDs)
#> Distribution stats (mean/skewness/kurtosis/p-value) available in $shrink
#> Minimization message ($message):
#> false convergence (8)
#> In an ODE system, false convergence may mean "useless" evaluations were performed.
#> See https://tinyurl.com/yyrrwkce
#> It could also mean the convergence is poor, check results before accepting fit
#> You may also try a good derivative free optimization:
#> nlmixr(...,control=list(outerOpt="bobyqa"))
#>
#> ── Fit Data (object is a modified tibble): ────────────────────────────────
#> # A tibble: 483 x 42
#> ID TIME DV EVID CMT PRED RES WRES IPRED IRES IWRES CPRED
#> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 0.5 0 0 cp 1.35 -1.35 -0.448 0.444 -0.444 -1.81 0.957
#> 2 1 1 1.9 0 cp 3.81 -1.91 -0.634 1.46 0.442 1.46 2.98
#> 3 1 2 3.3 0 cp 8.07 -4.77 -1.51 3.98 -0.681 -1.20 7.35
#> # … with 480 more rows, and 30 more variables: CRES <dbl>, CWRES <dbl>,
#> # eta.ktr <dbl>, eta.ka <dbl>, eta.cl <dbl>, eta.v <dbl>,
#> # eta.emax <dbl>, eta.ec50 <dbl>, eta.kout <dbl>, eta.e0 <dbl>,
#> # ktr <dbl>, ka <dbl>, cl <dbl>, v <dbl>, logit <dbl>, emax <dbl>,
#> # ec50 <dbl>, kout <dbl>, e0 <dbl>, DCP <dbl>, PD <dbl>, kin <dbl>,
#> # cp <dbl>, depot <dbl>, gut <dbl>, center <dbl>, effect <dbl>,
#> # EPRED <dbl>, ERES <dbl>, NPDE <dbl>
plot(fit.TOF)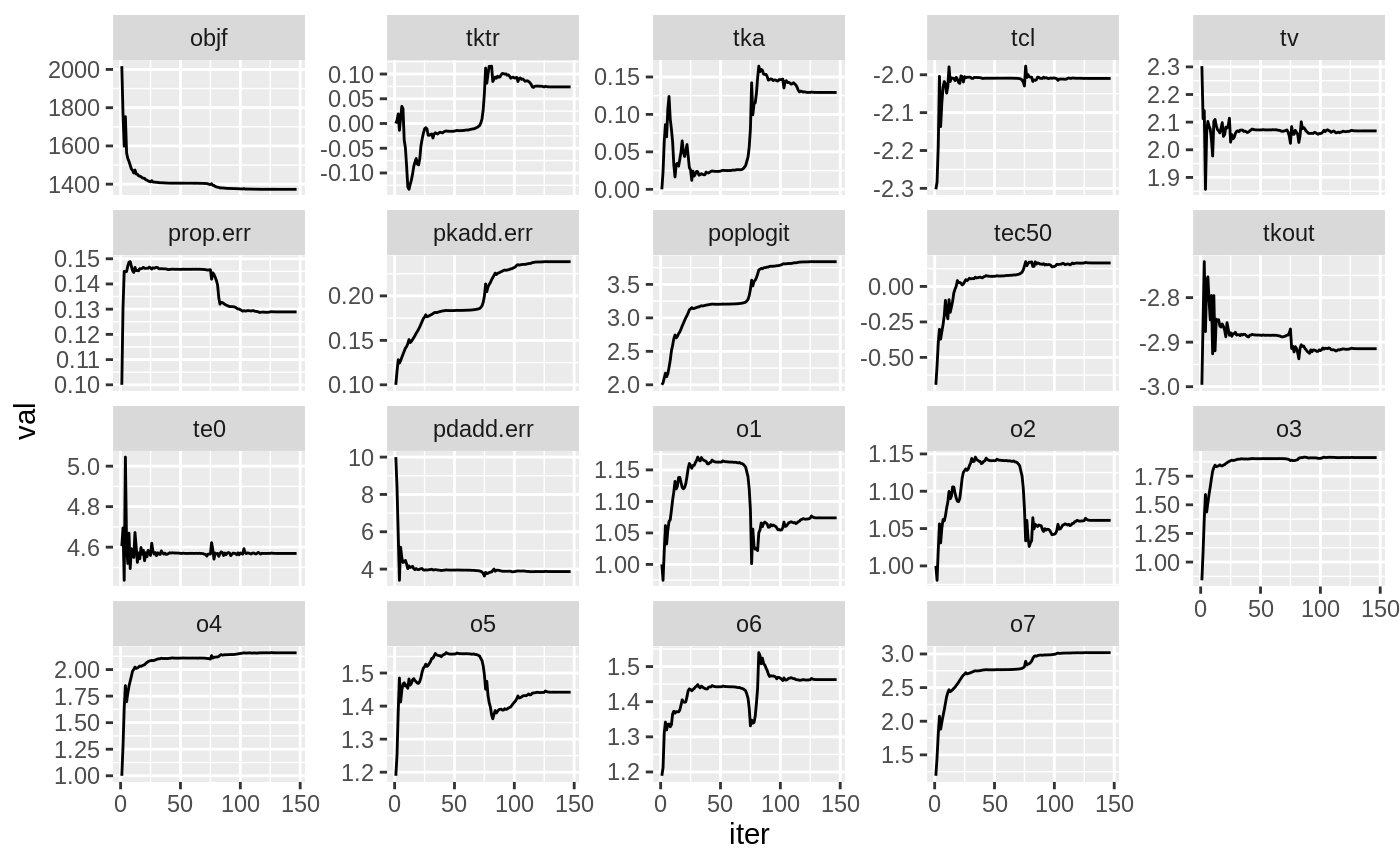
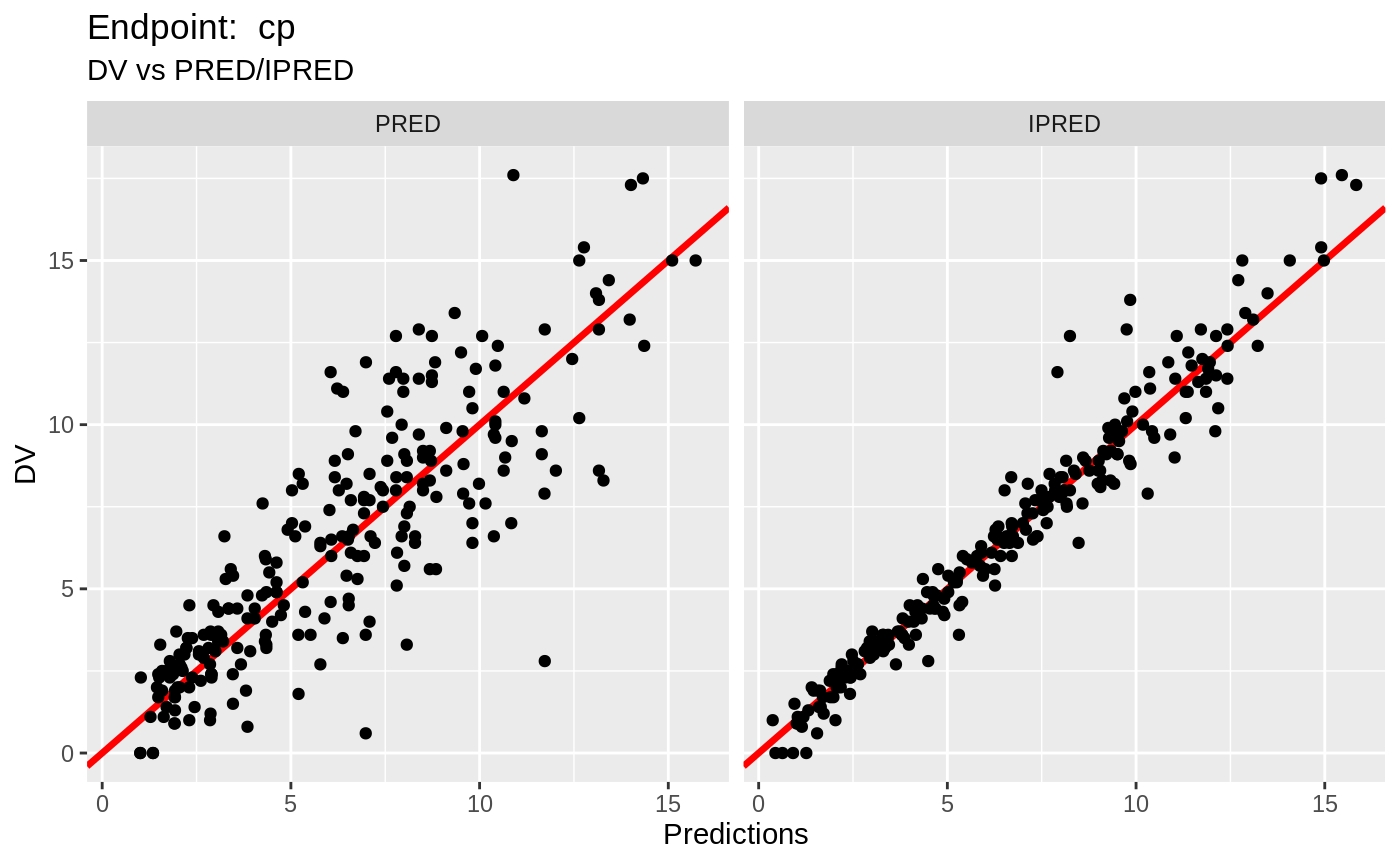
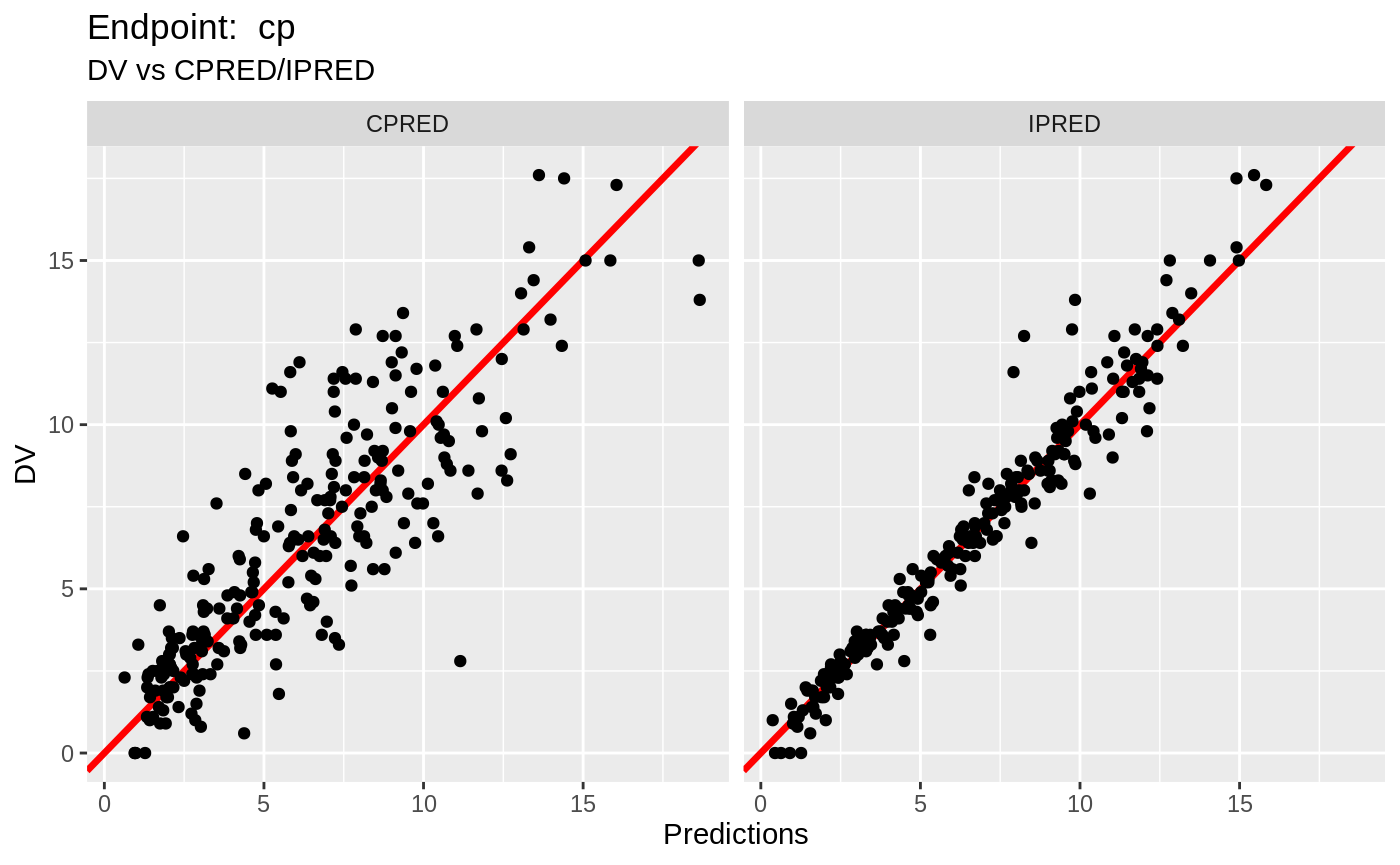
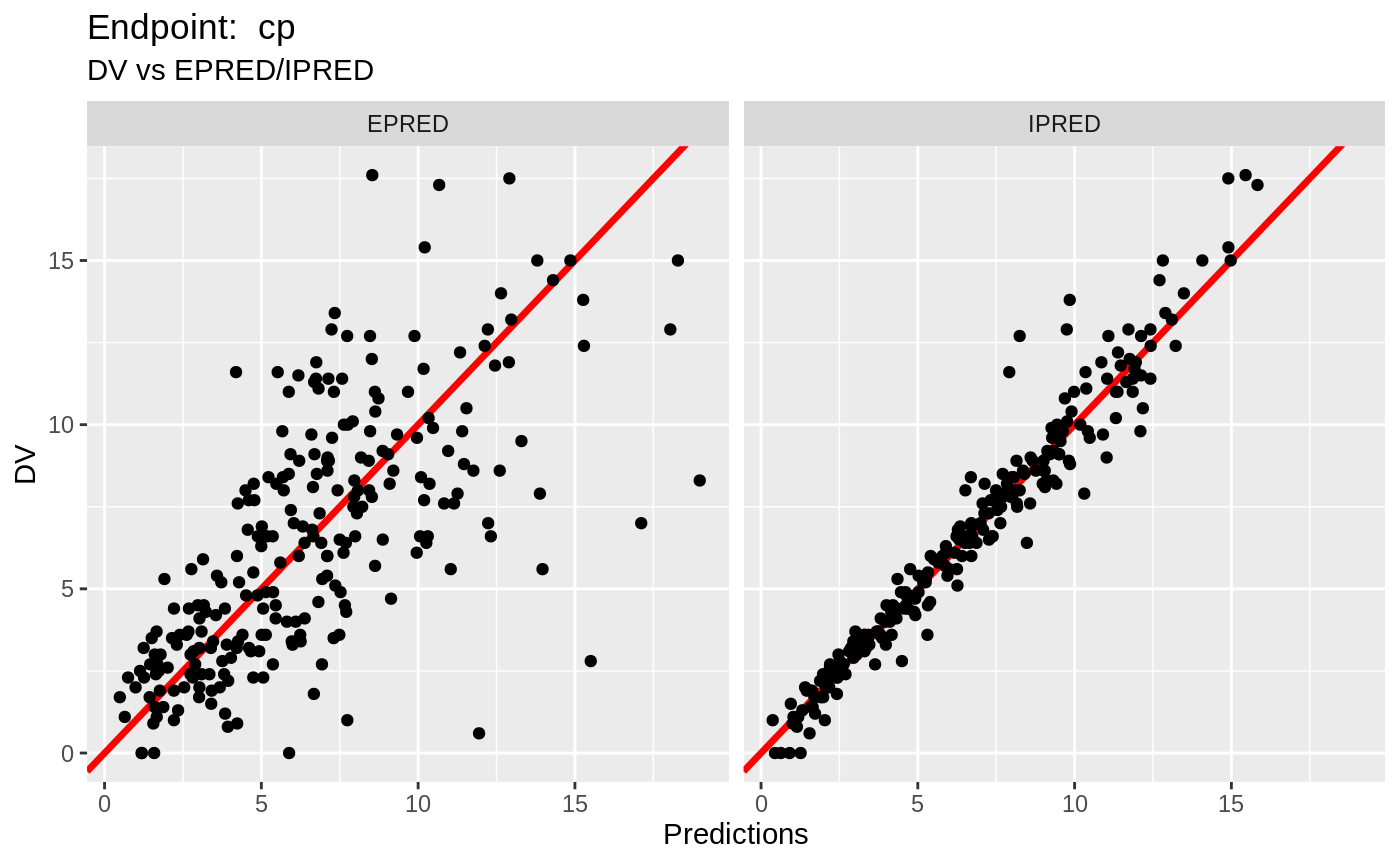
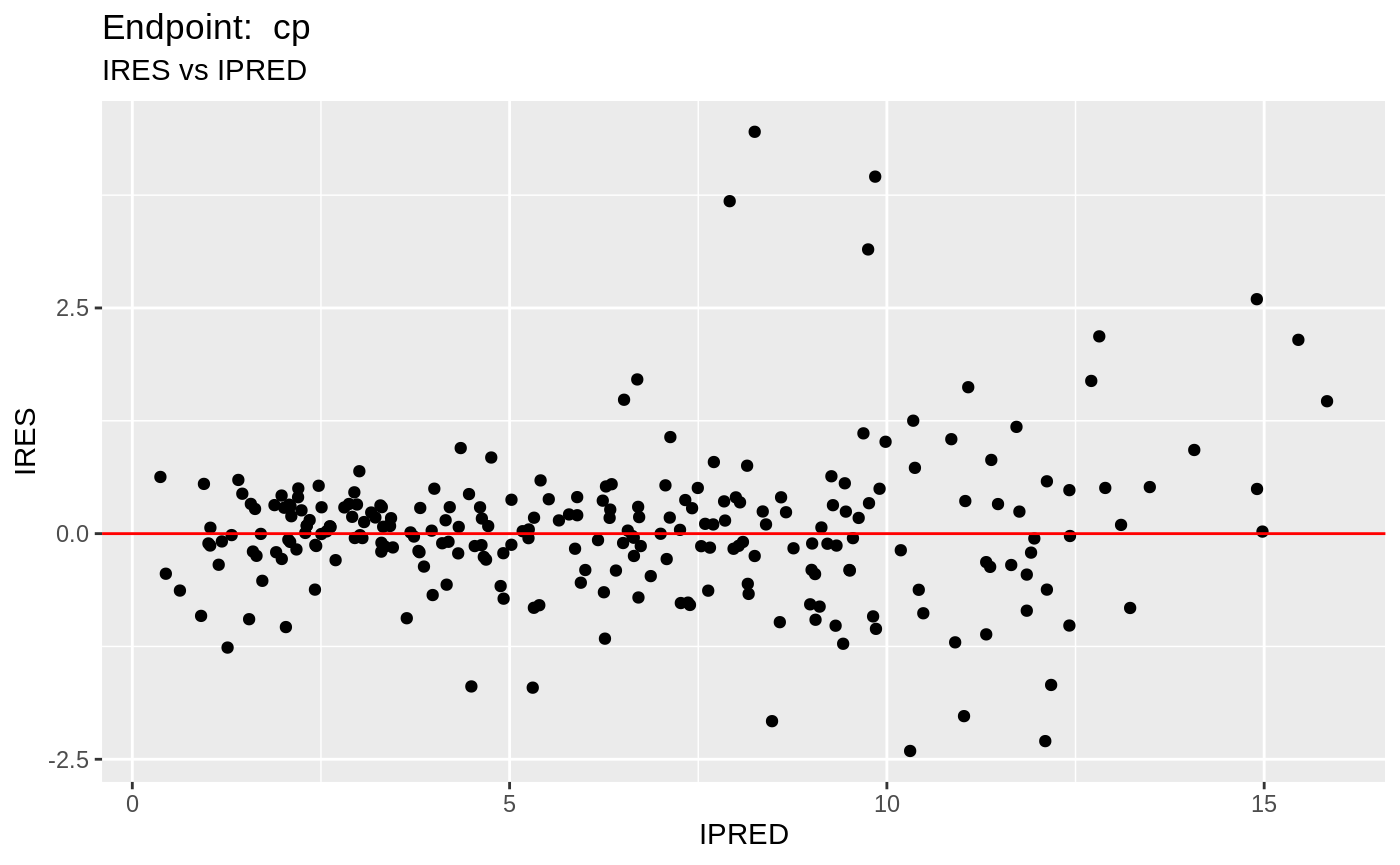
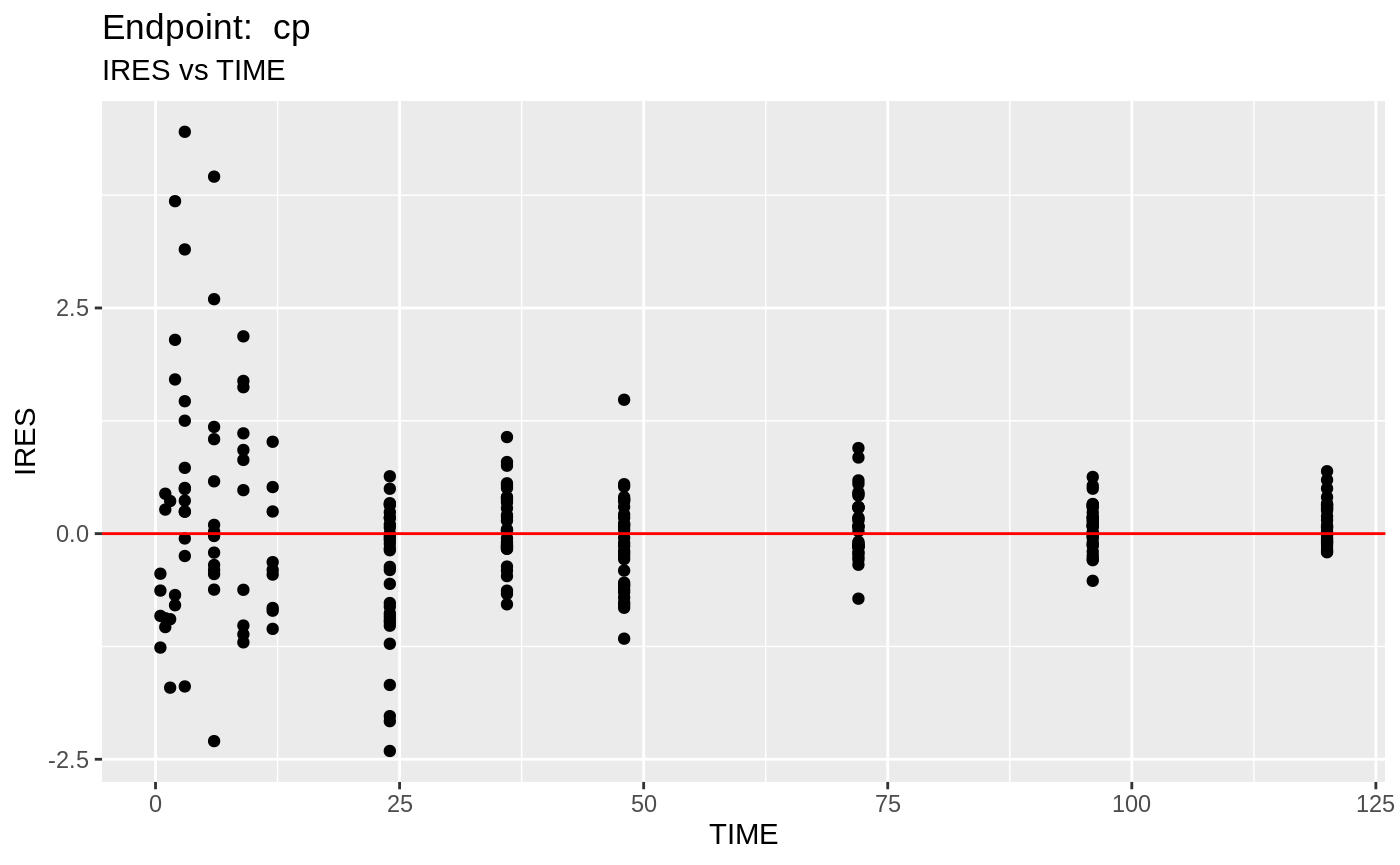
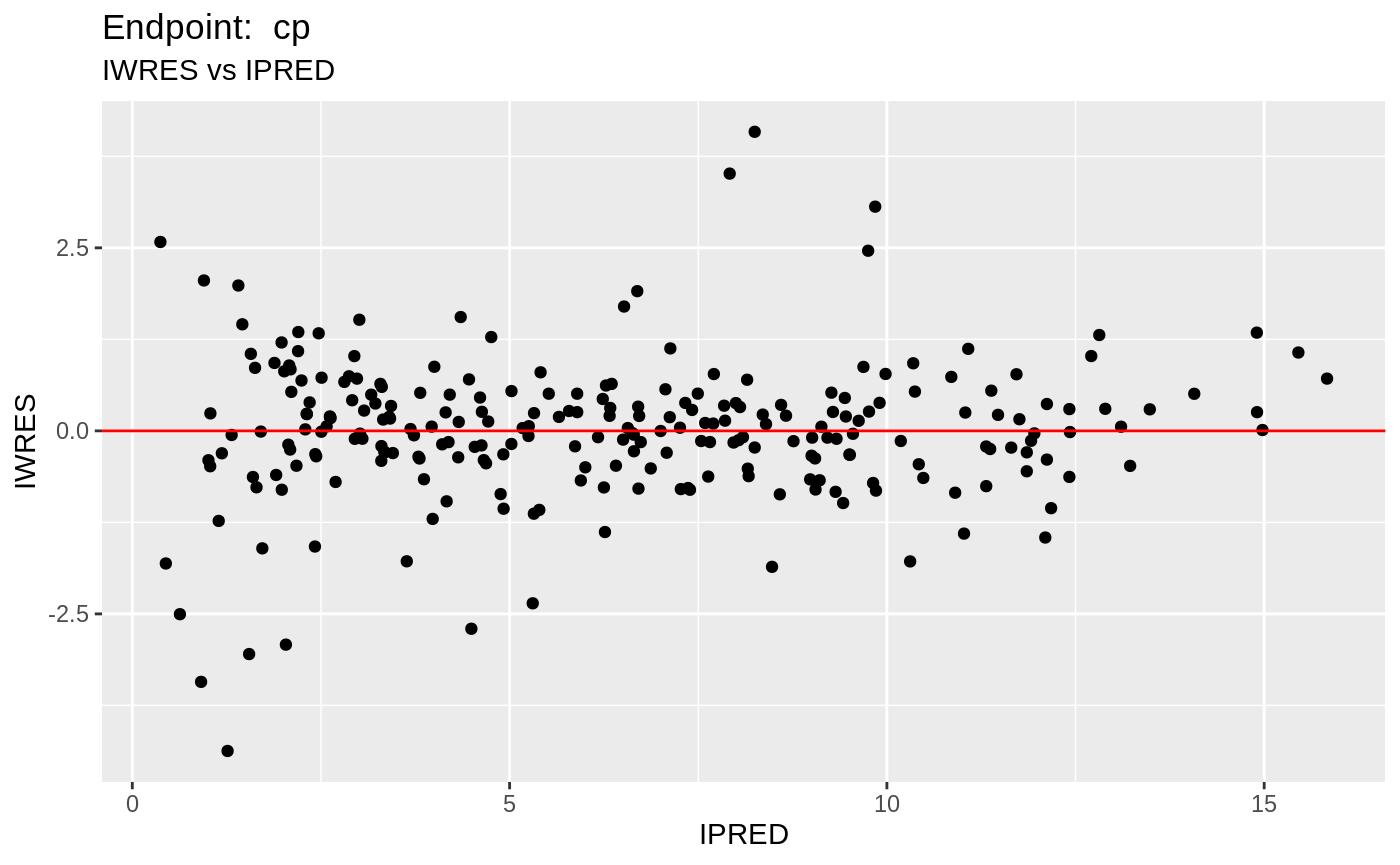
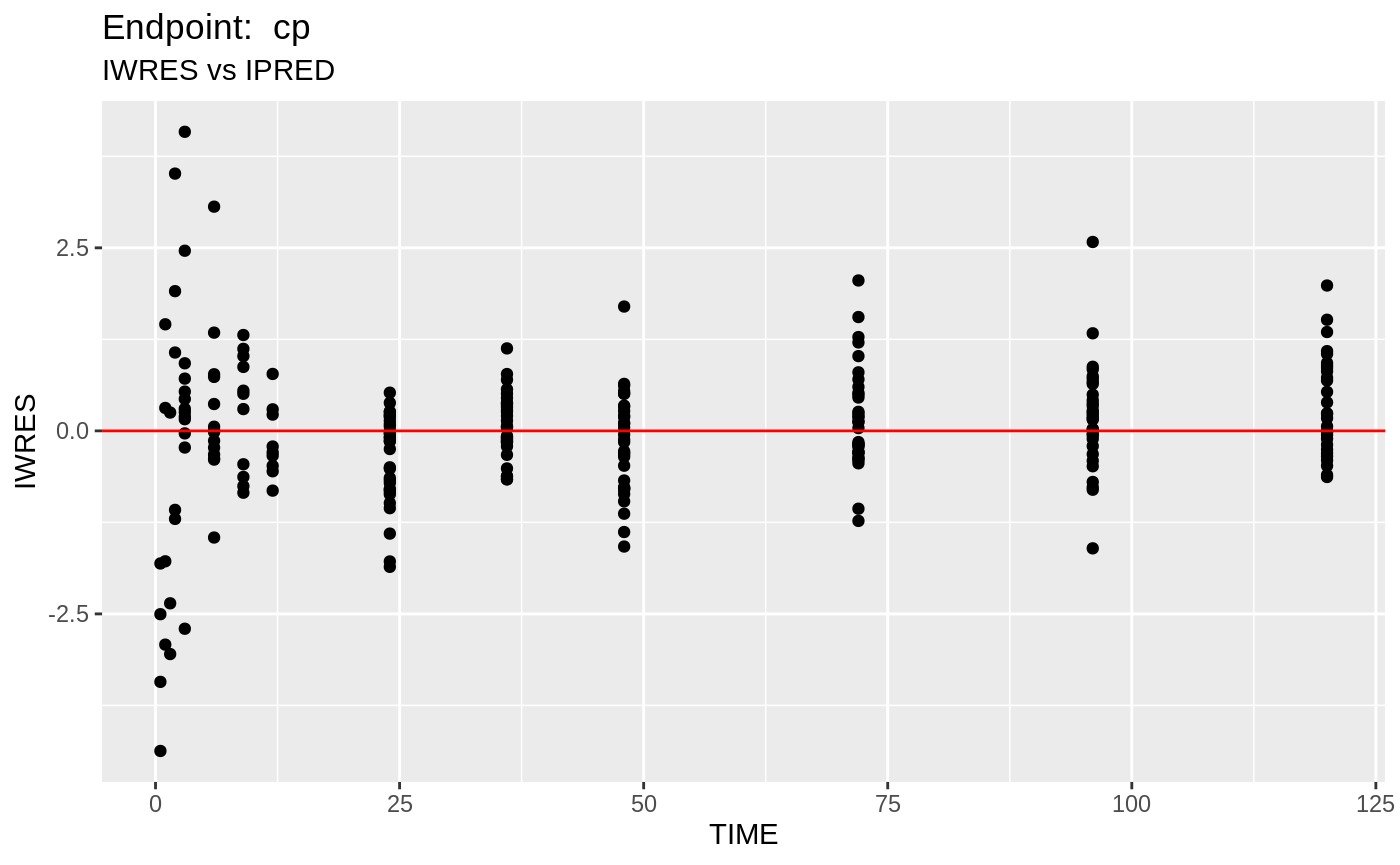
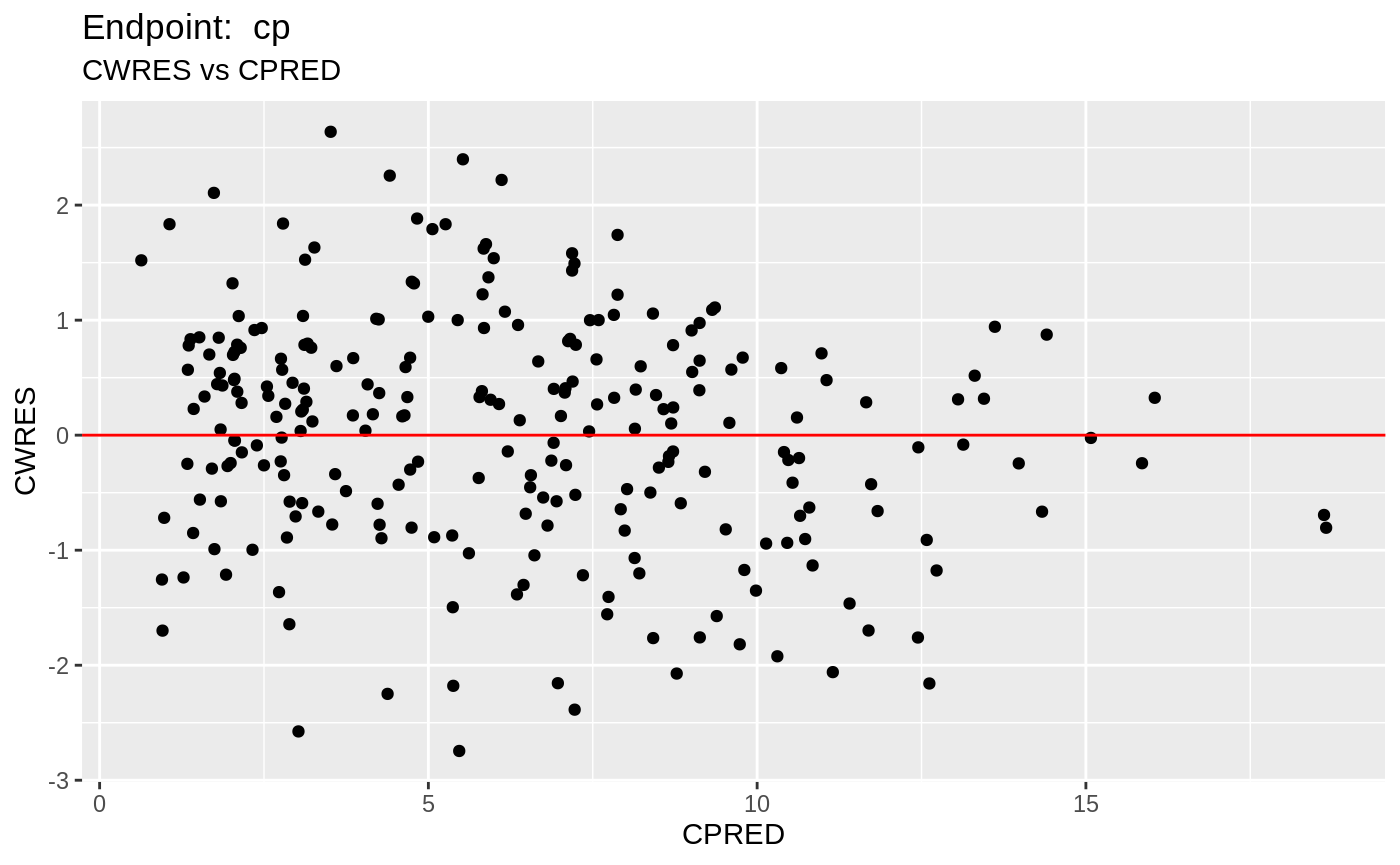
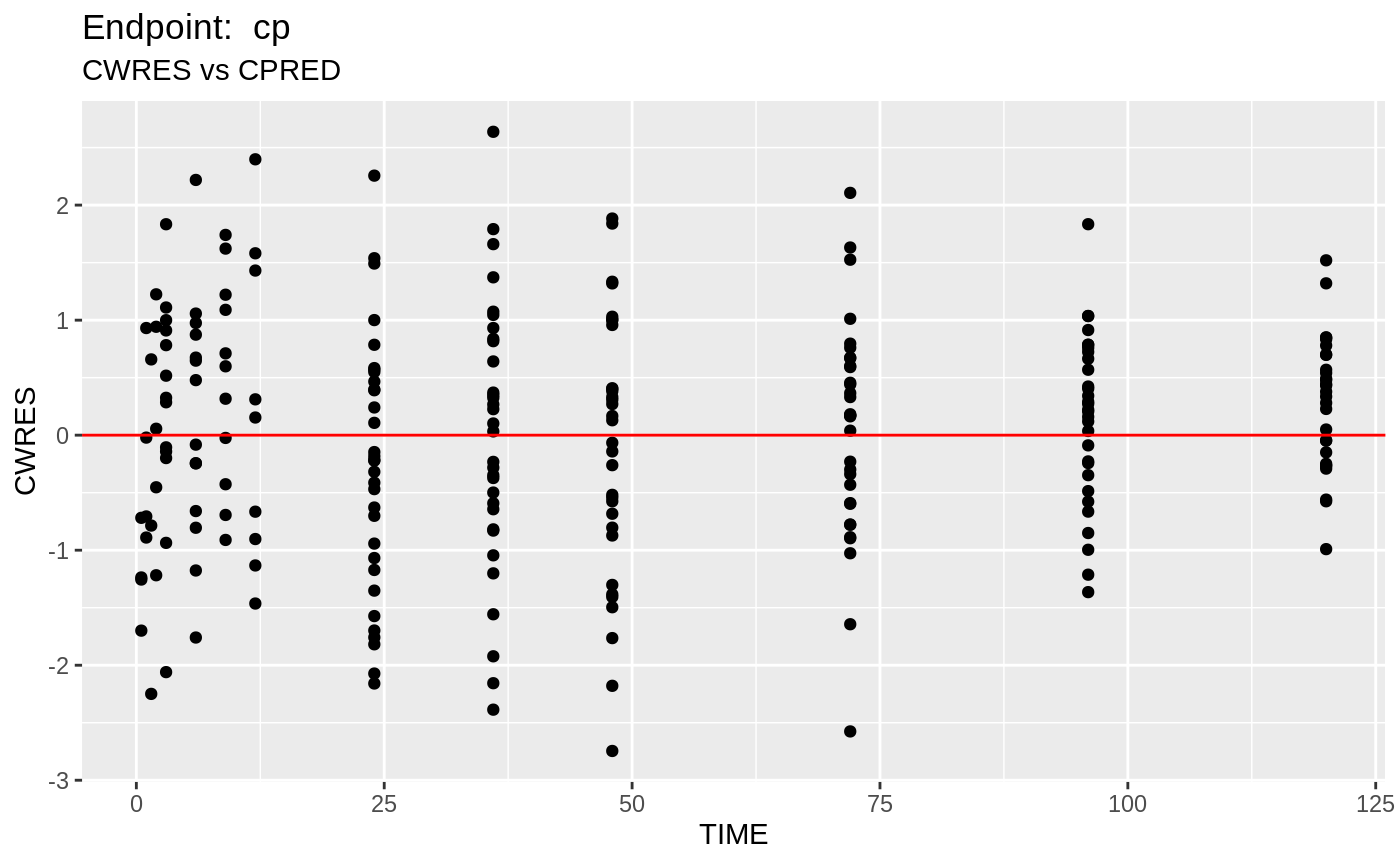
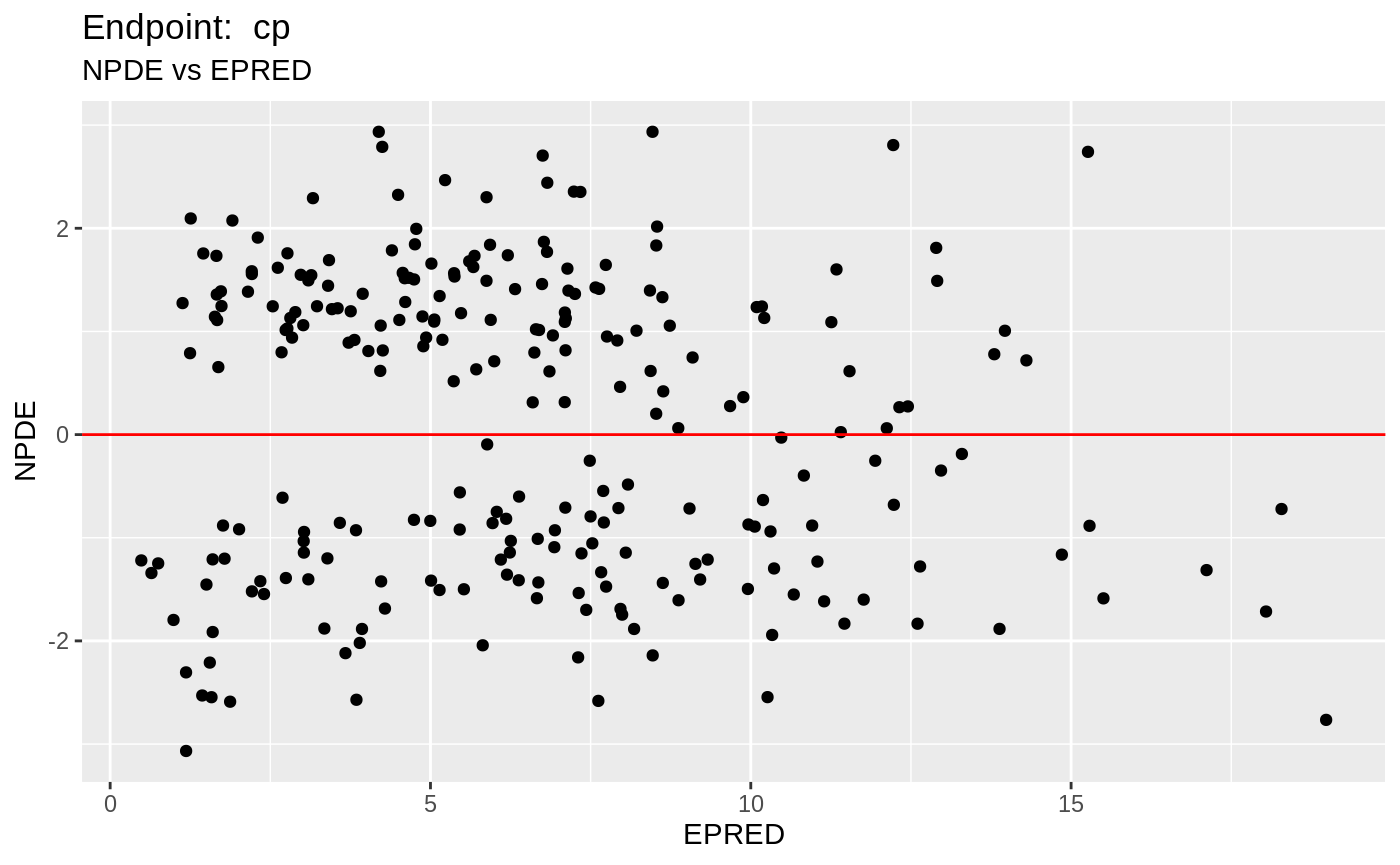
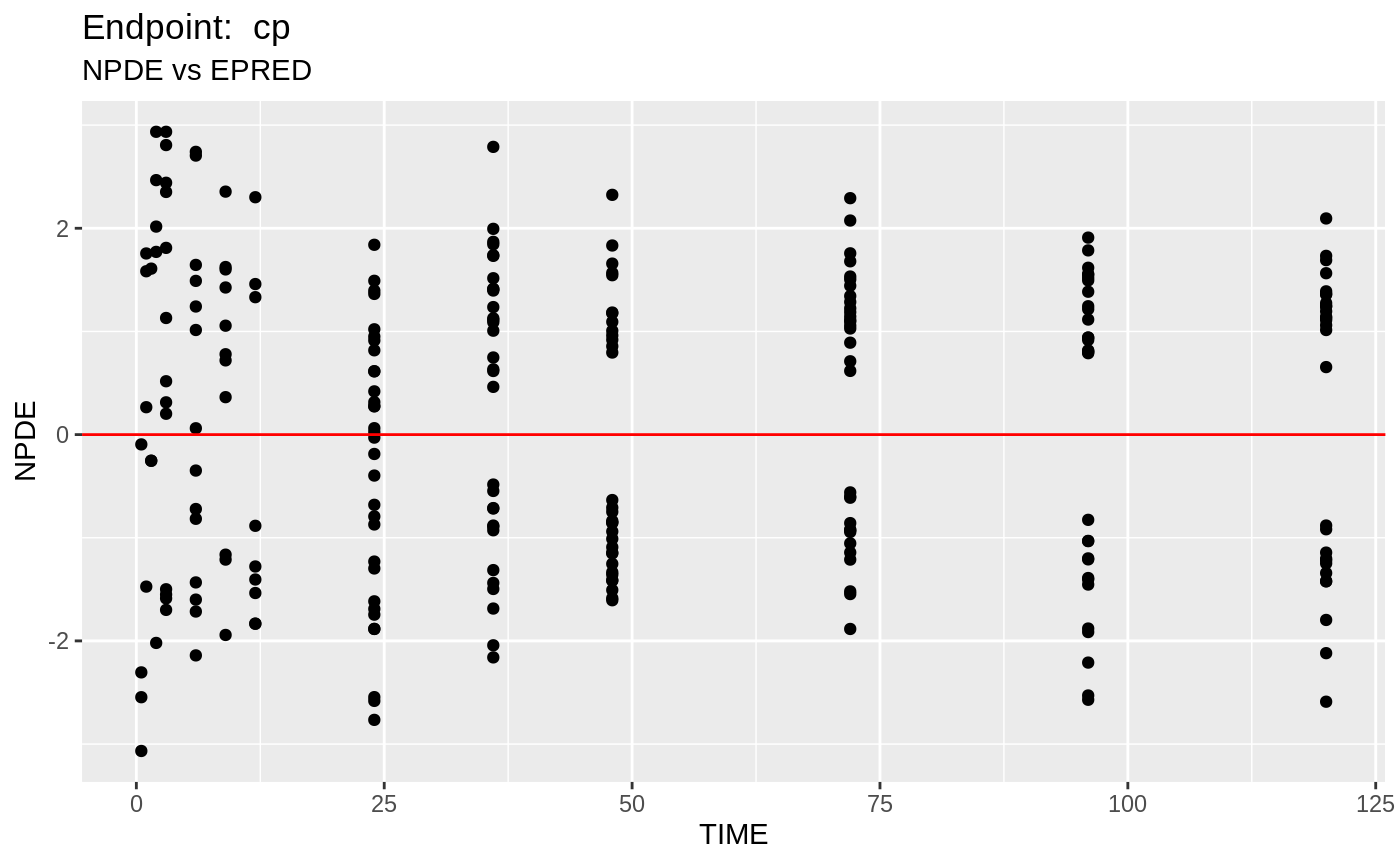
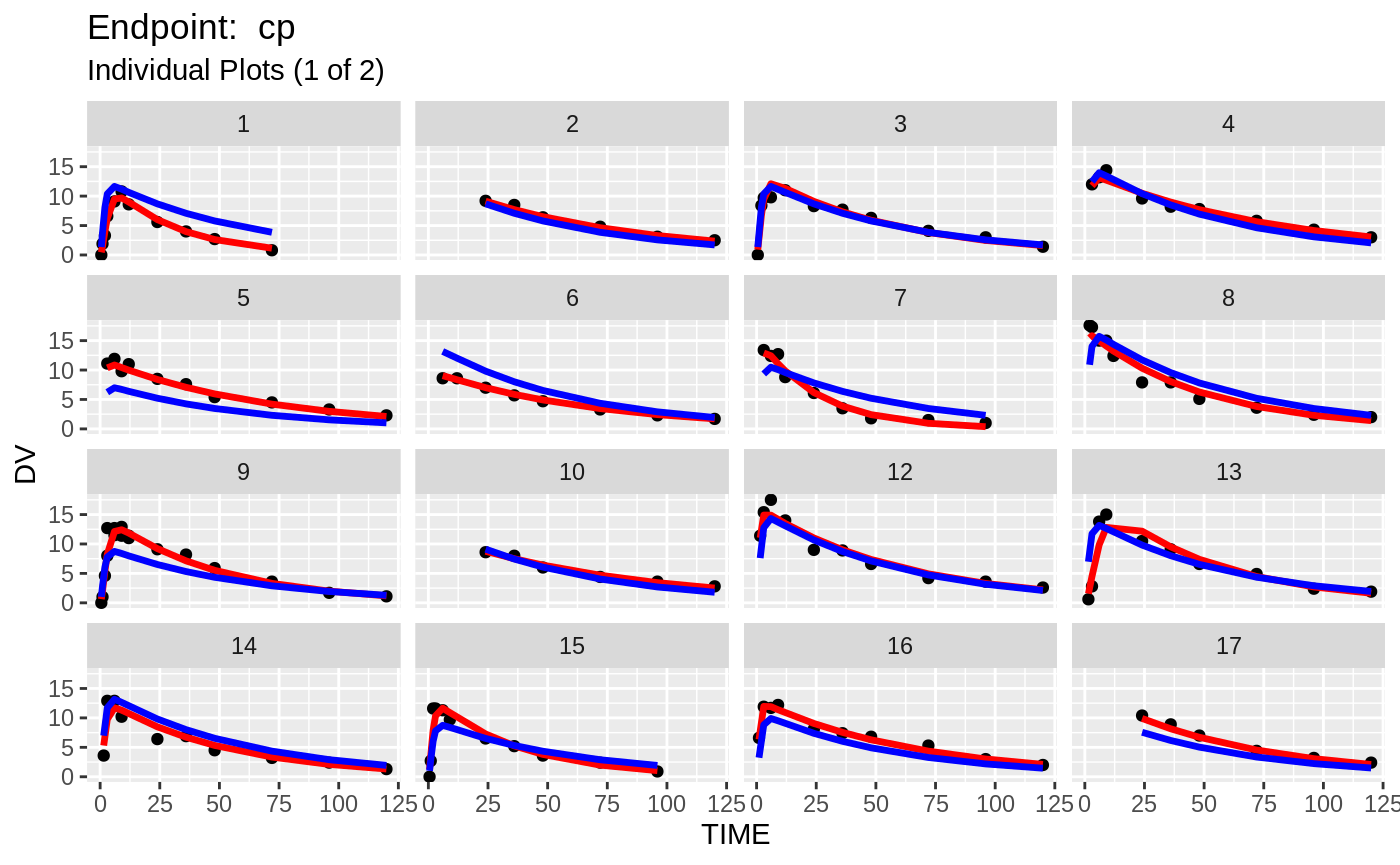
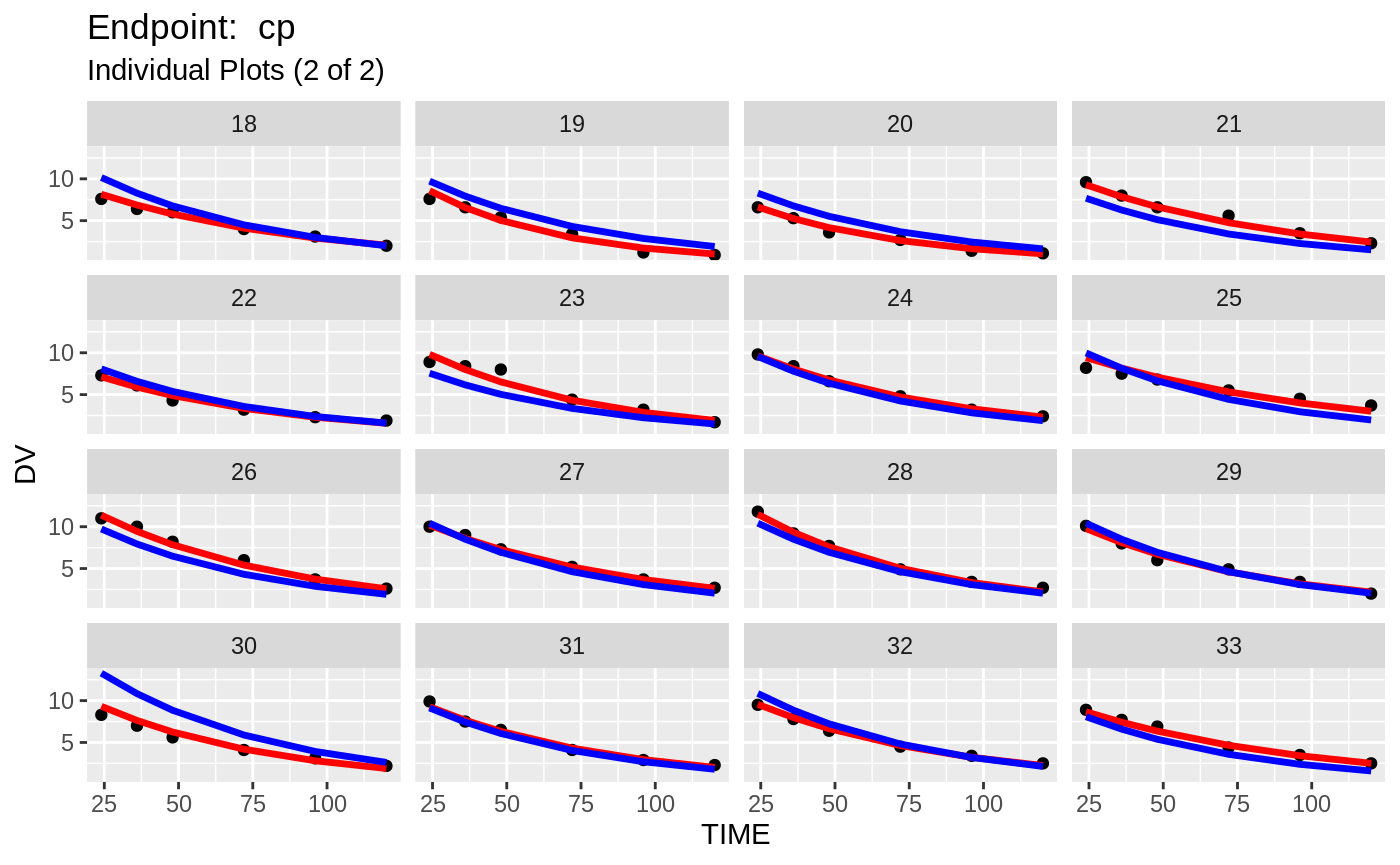
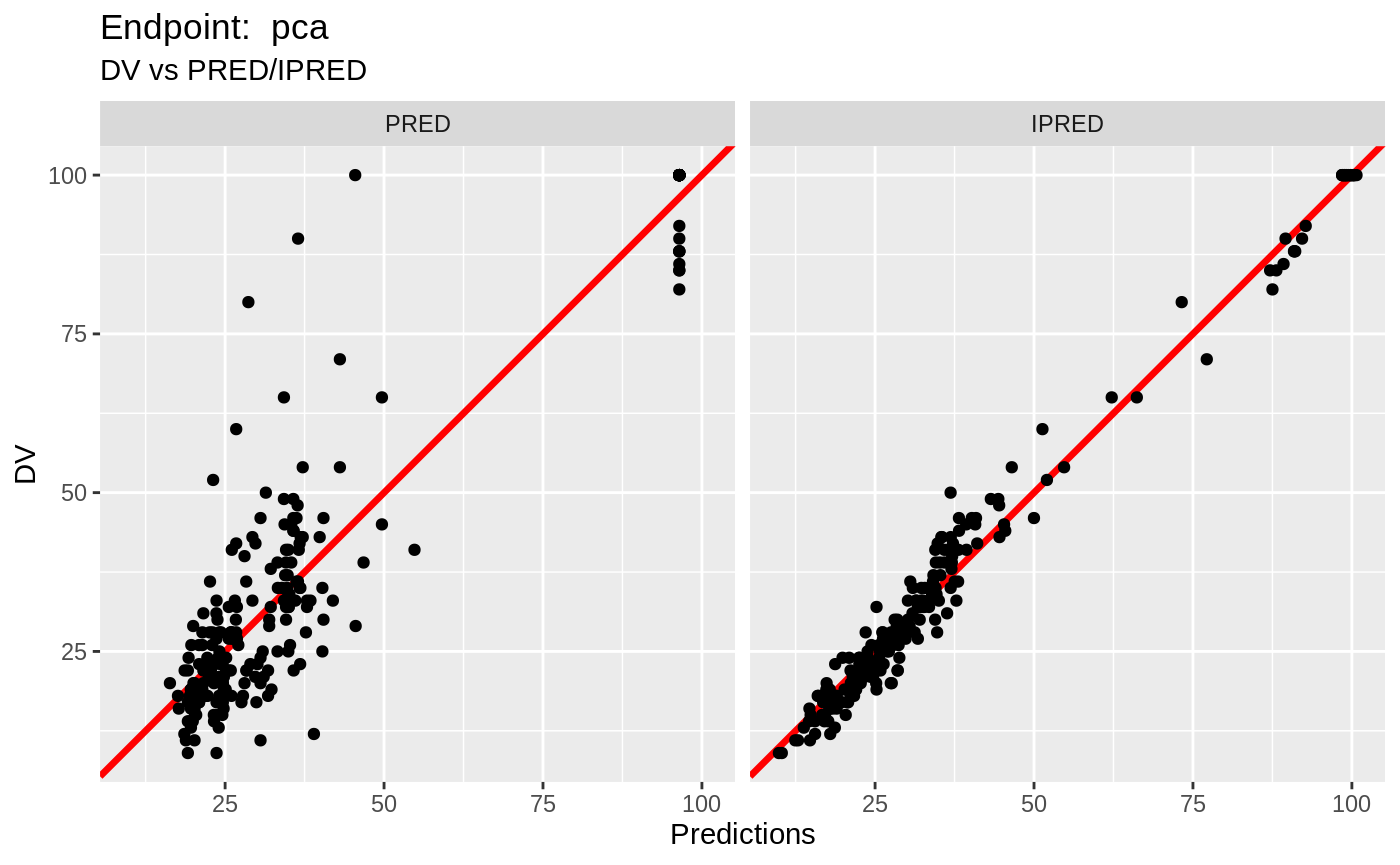
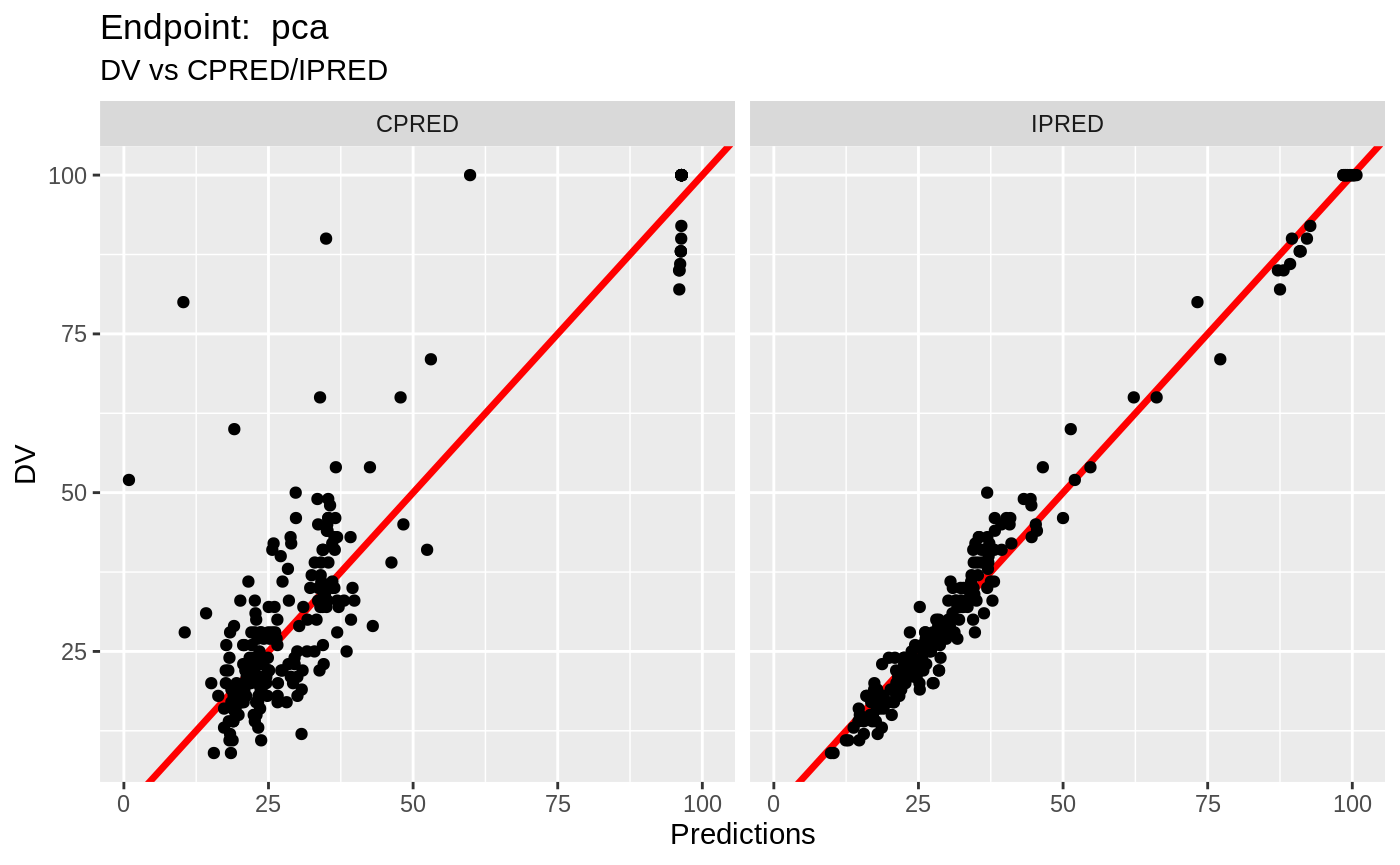
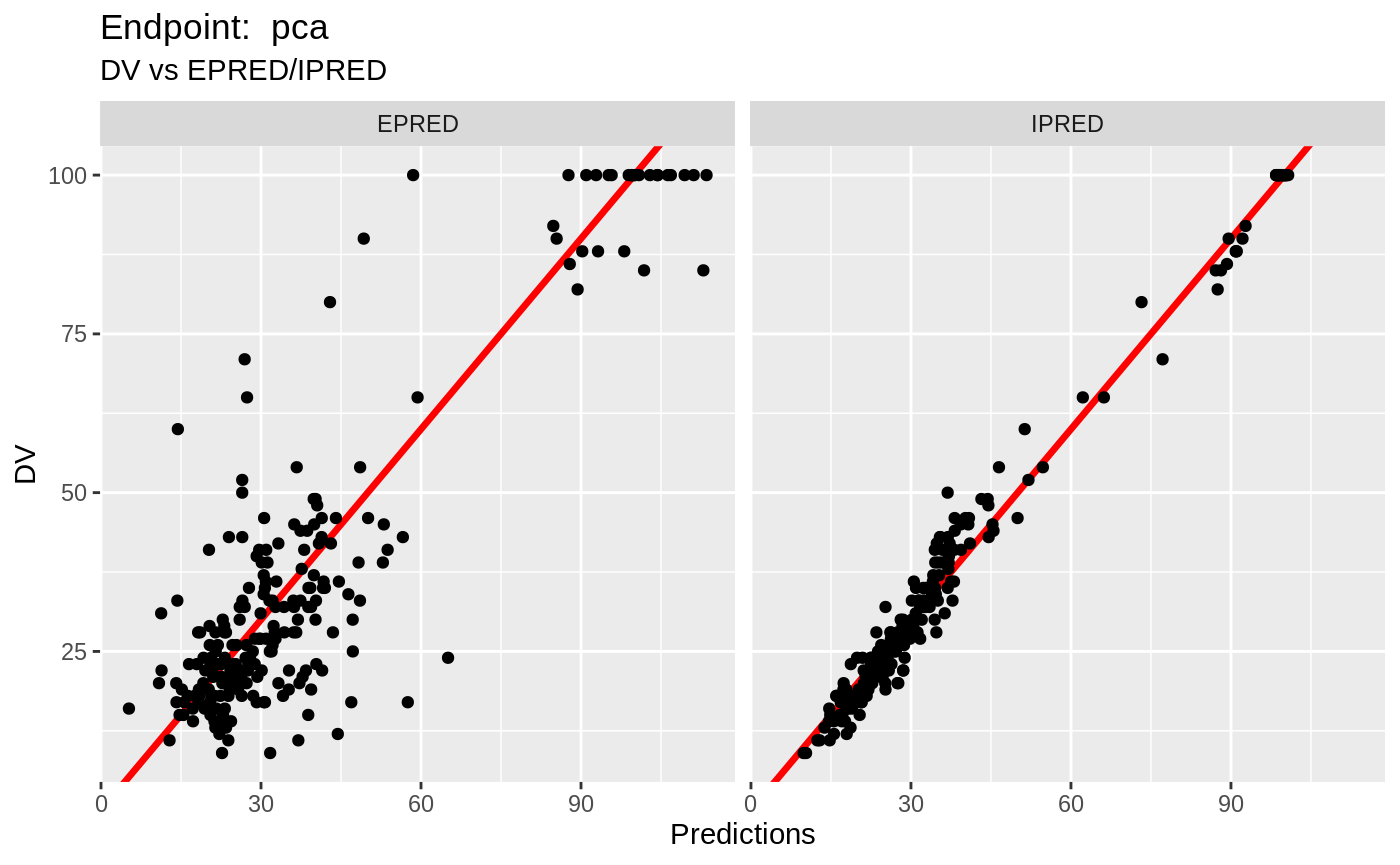
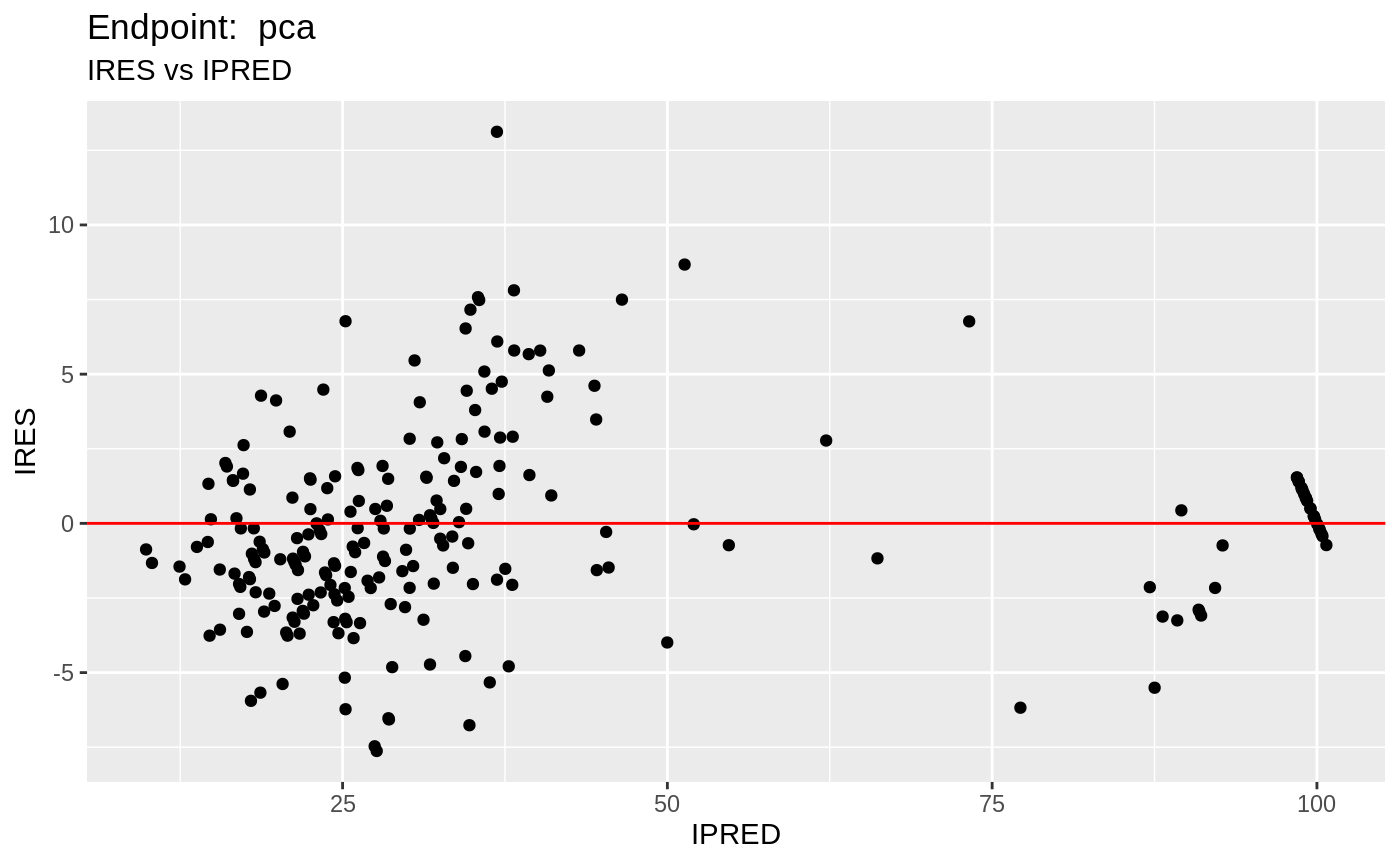
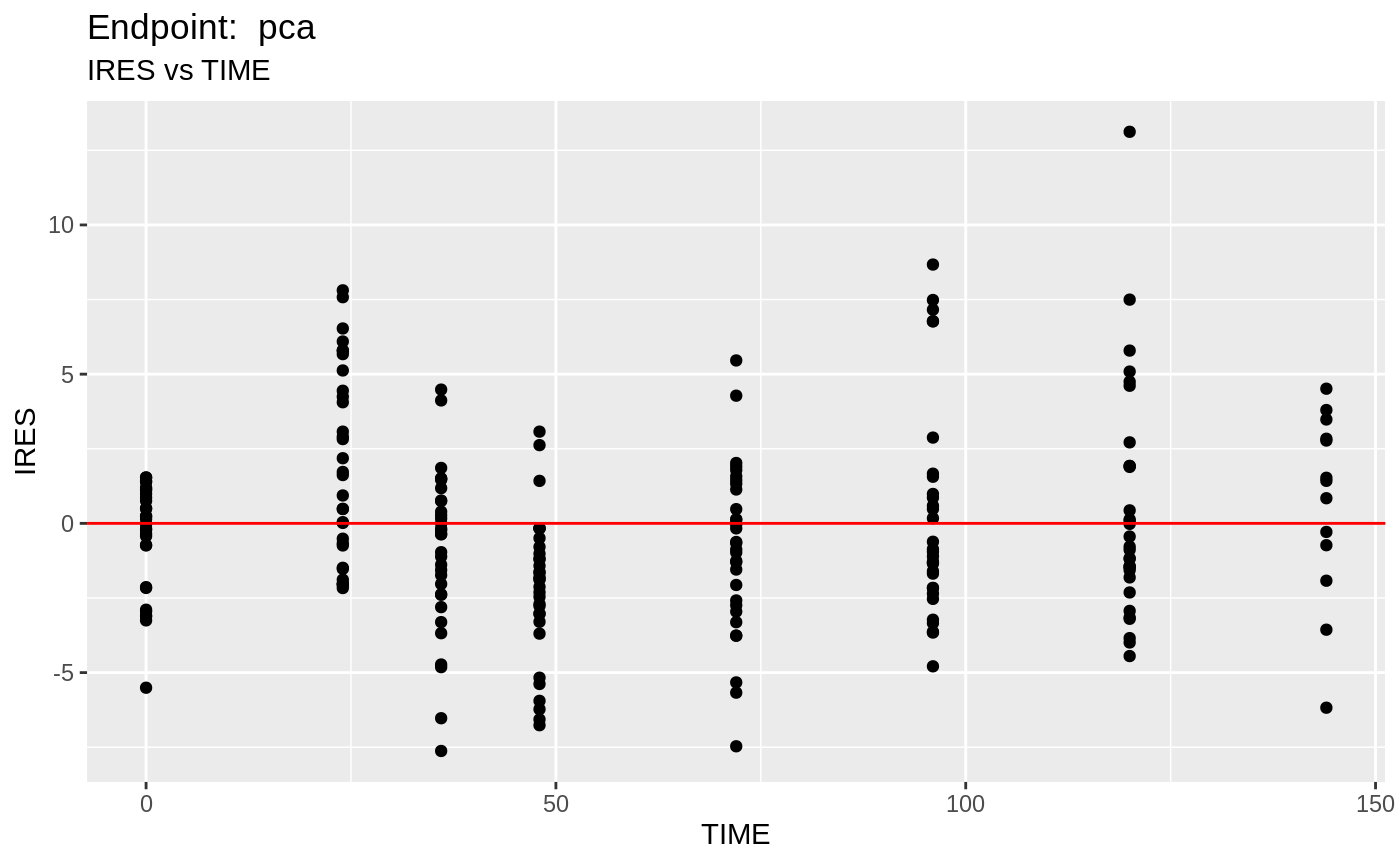
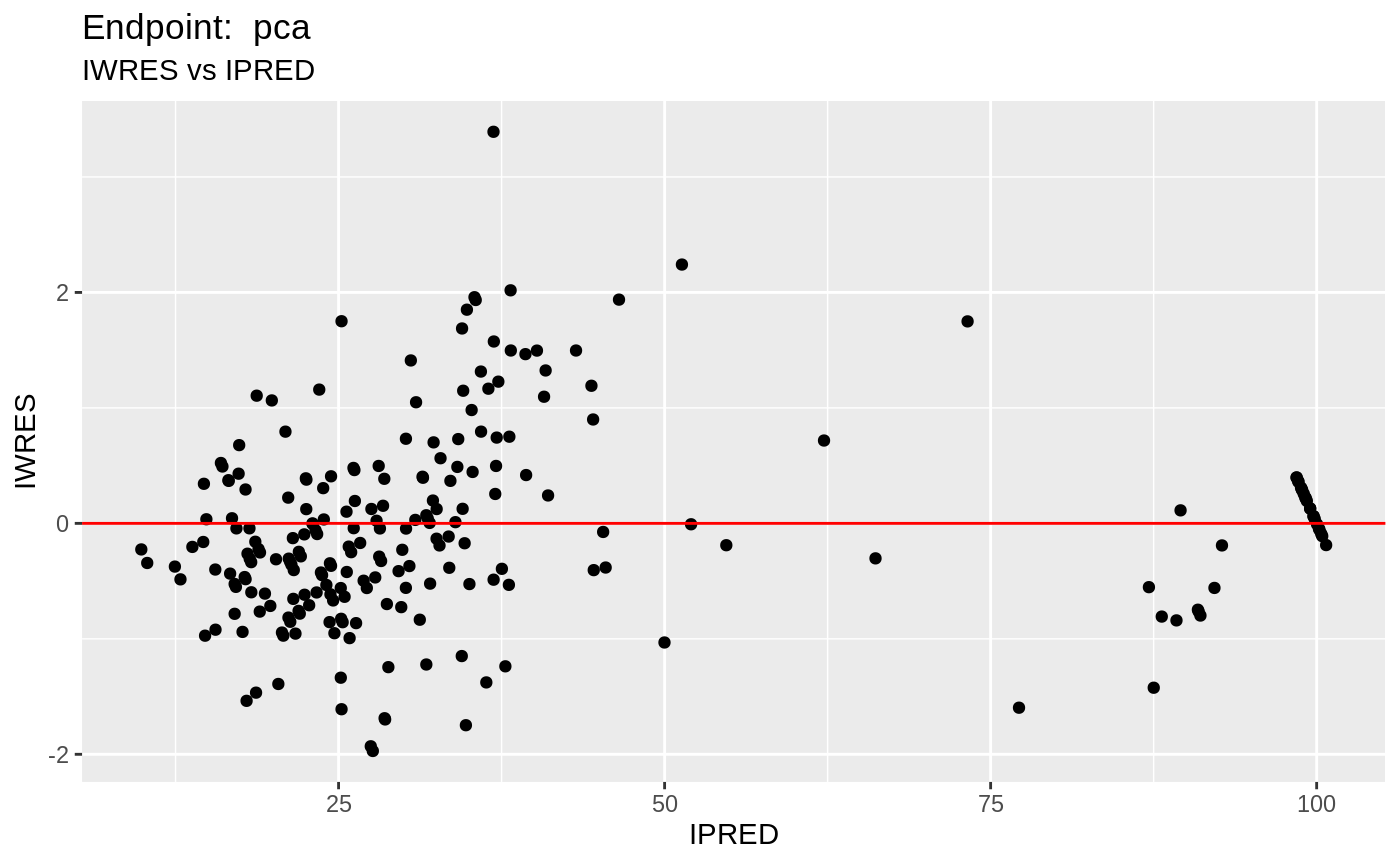
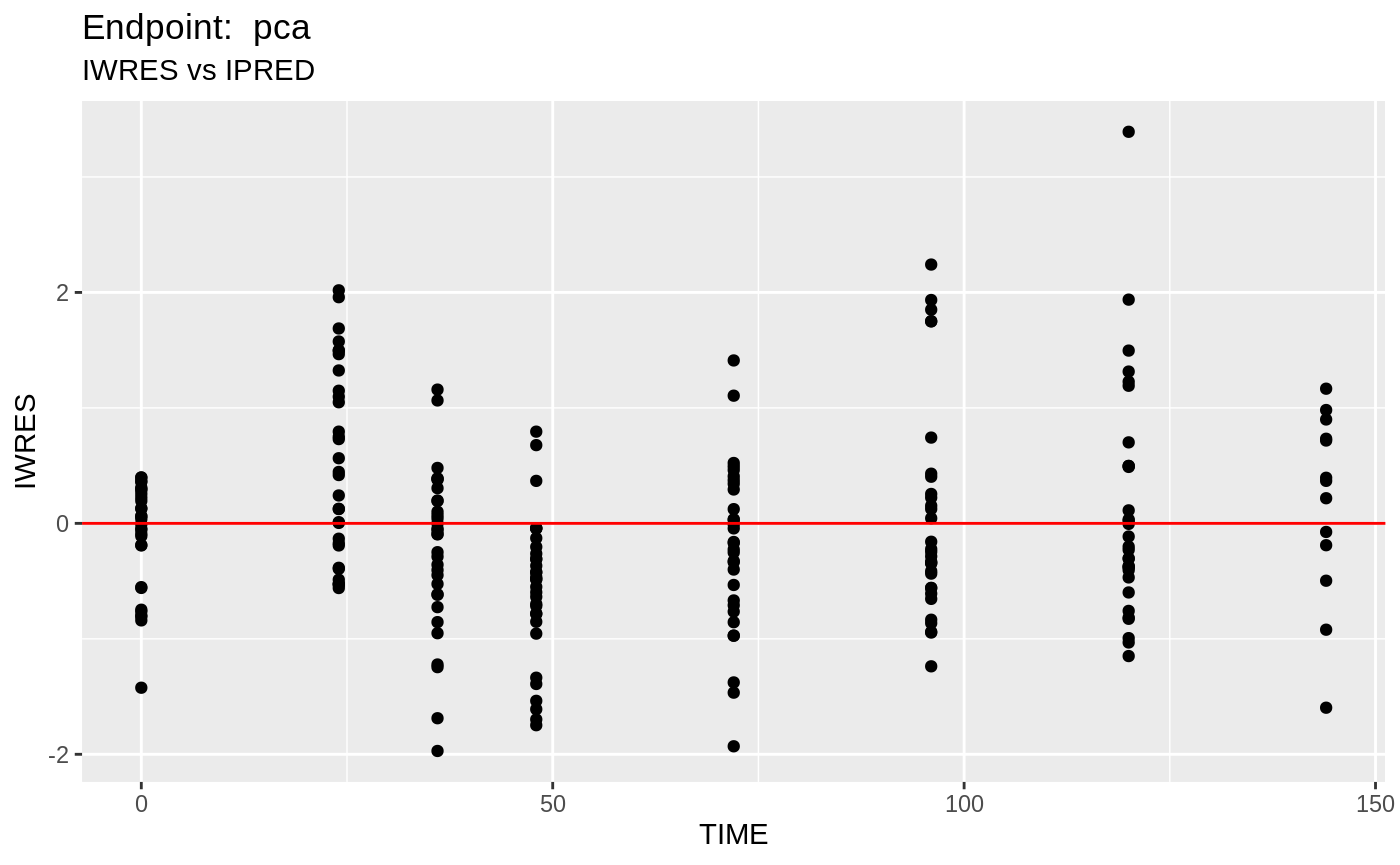
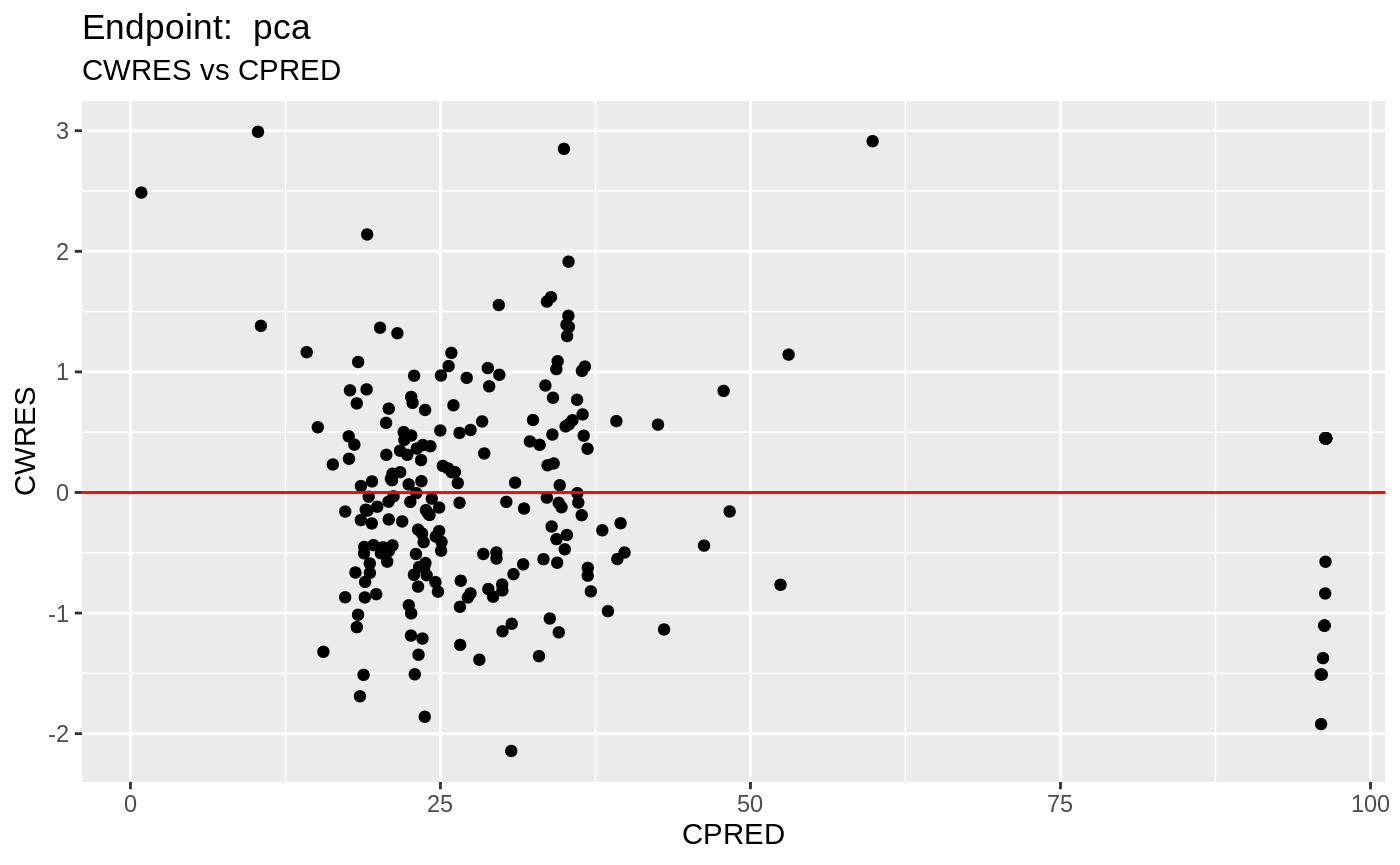
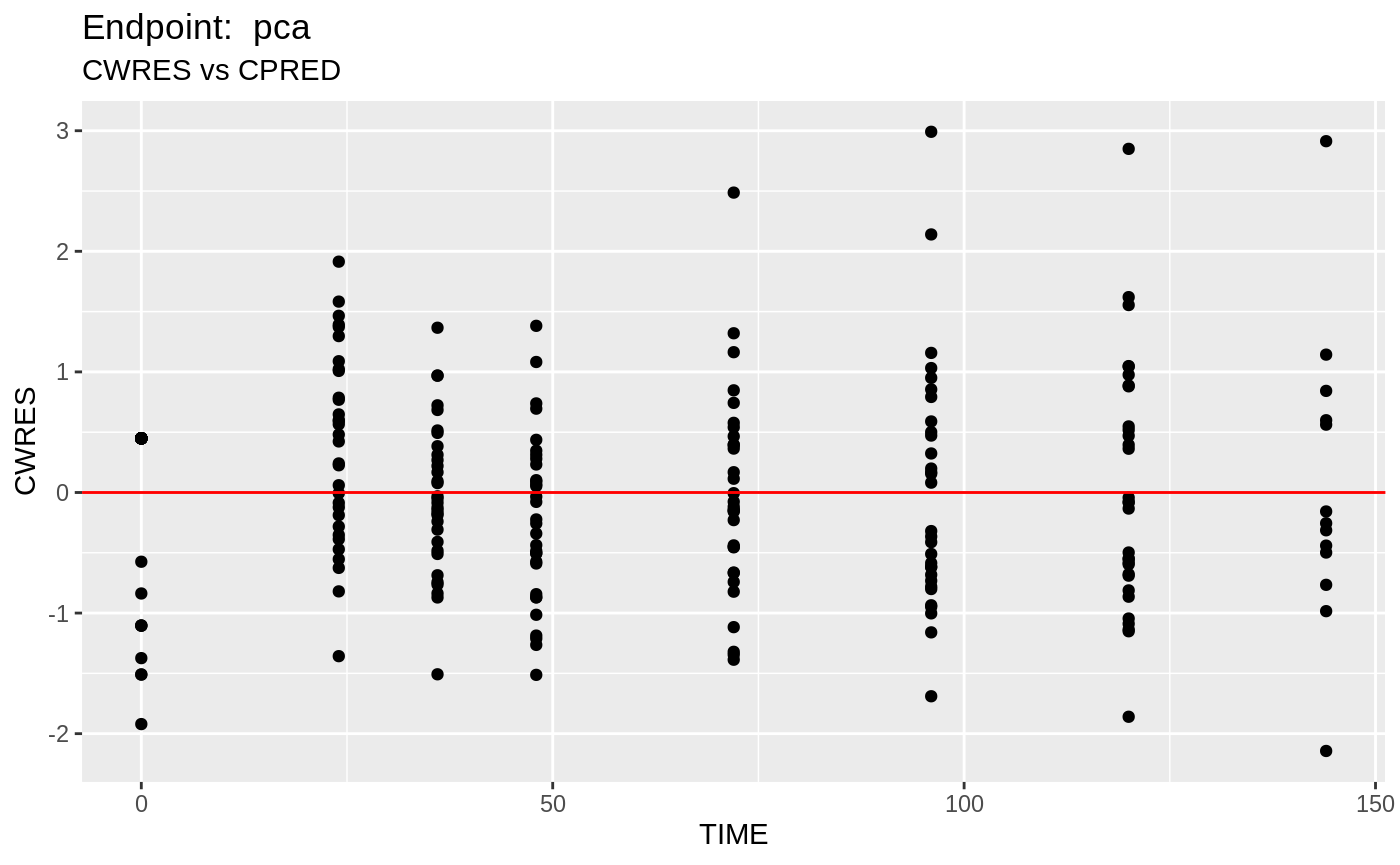
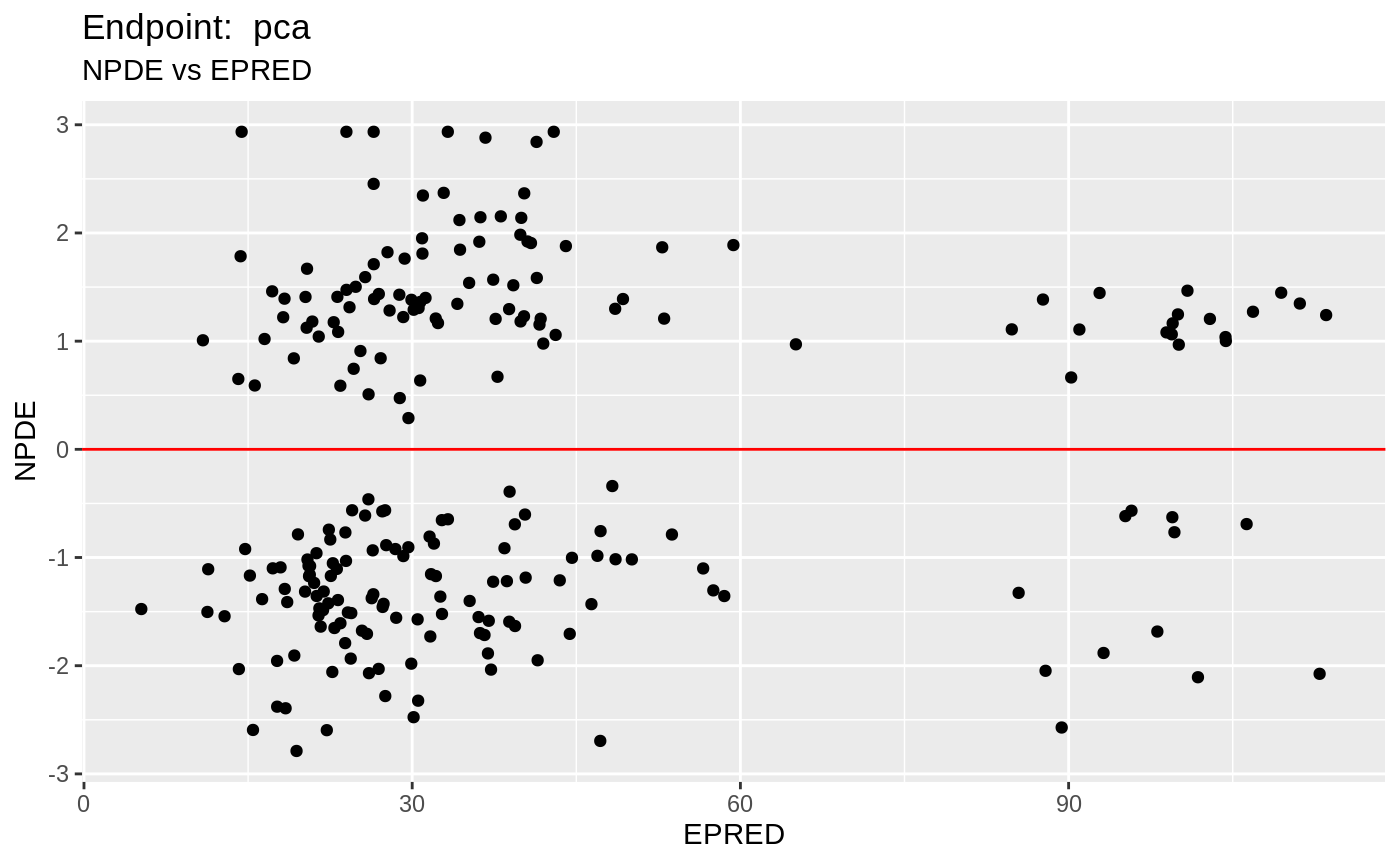
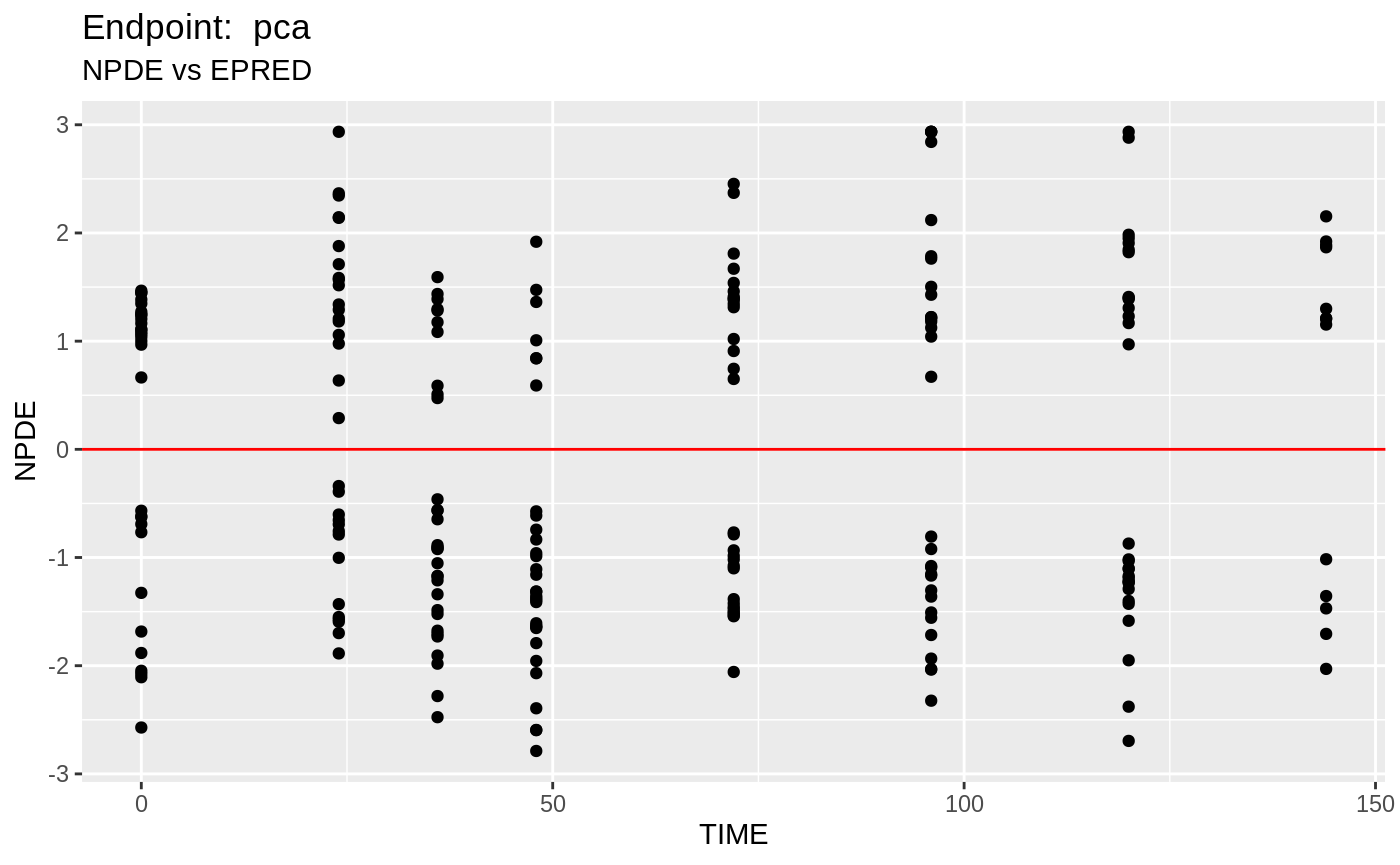
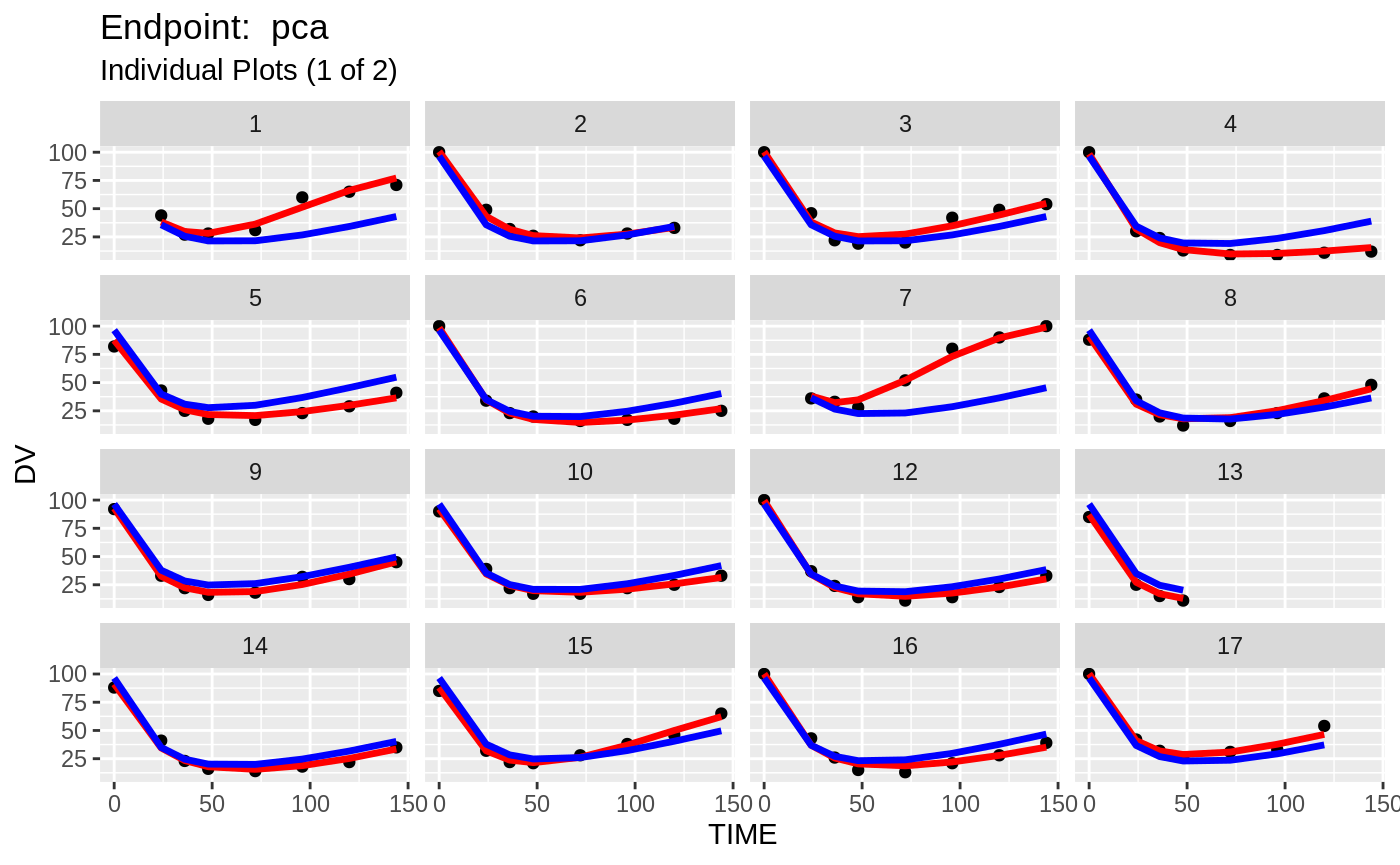
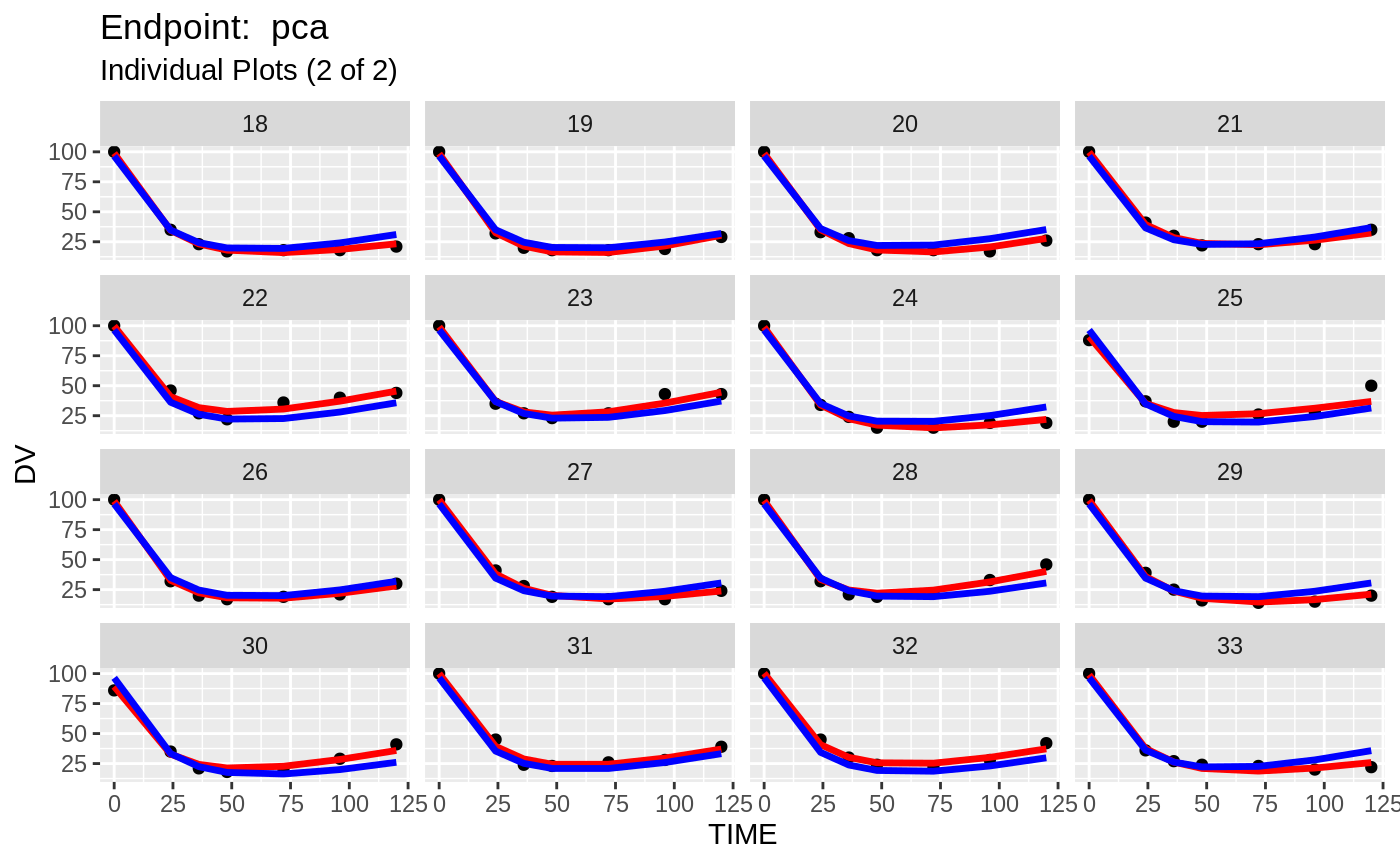
v1f <- nlmixr::vpc(fit.TOF, show=list(obs_dv=T), scales="free_y") +
ylab("Warfarin Cp [mg/L] or PCA") +
xlab("Time [h]");
v2f <- nlmixr::vpc(fit.TOF, show=list(obs_dv=T), pred_corr = TRUE) +
ylab("Prediction Corrected Warfarin Cp [mg/L] or PCA") +
xlab("Time [h]")
gridExtra::grid.arrange(v1f, v2f)